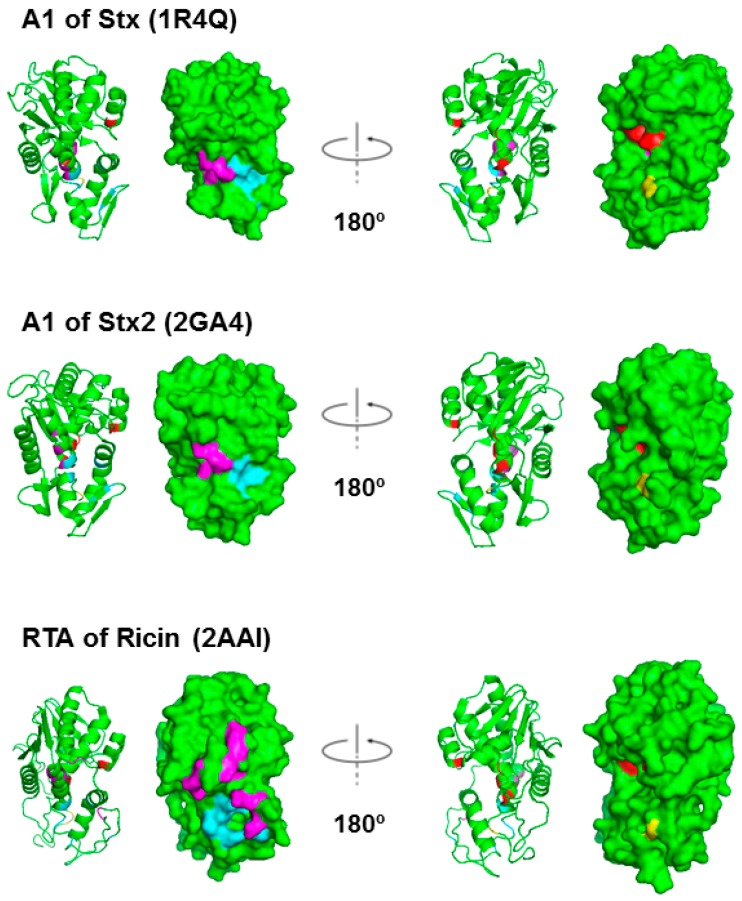
Figure 2.
Structures of the StxA1, Stx2A1 and RTA shown as ribbon and as surface. The residues at the active site, Tyr76/Tyr77, Tyr114, Glu167 and Arg170 in Stx; Tyr80, Tyr123, Glu177 and Arg180 in RTA, are shown in red. The arginines that are critical for P protein interaction, Arg172, Arg176 and Arg179 in Stxs and Arg189, Arg191, Arg193, Arg196, Arg197, Arg234 and Arg235 in RTA, are shown in magenta. The residues that form a hydrophobic pocket and interact with the last six residues of the P-proteins, Gln173, Leu198, Ile224/Ile223, Phe226/Phe225, Leu233/Leu232, Ser235/Thr234 in Stx/Stx2 and Tyr183, Leu207, Phe240, Ile247, Pro250 and Ile251 in RTA, are shown in cyan [29]. Cys242/241 in Stx/Stx2 A1, which form a disulfide bond with Cys261/260 in Stx/Stx2 A2, and Cys259 in RTA, which forms a disulfide bond with Cys2 in RTB, are shown in yellow. Stx PDB ID: 1R4Q, Stx2 PDB ID: 2RA4 and ricin PDB ID: 2AA1. The structures were generated using PyMOL.