Figure 4. Relationships between PTSD symptoms and neuropsychological performance and activation of the rostral ACC and medial PFC regions of interest.
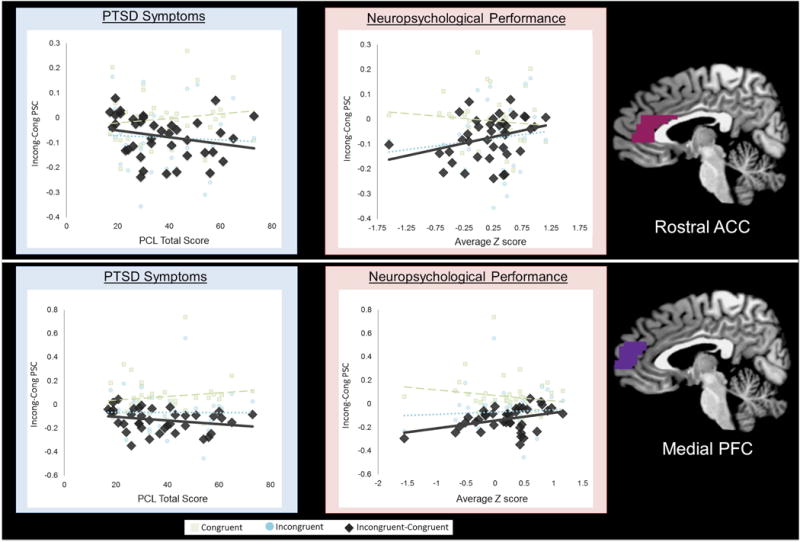
Extracted percent signal change from regions of interest indicate that worse PTSD symptoms (rostral ACC: ρ = −0.35, p = 0.031; medial PFC: NS. ρ = −0.30, p = .064) or neuropsychological performance (rostral ACC: r = 0.32, p = .048; medial PFC:r = 0.34, p = 0.032) relate to less differential activation (Incongruent-Congruent) during the multi source interference task, which was partially driven by increased activation during congruent trials.
