Figure 2.
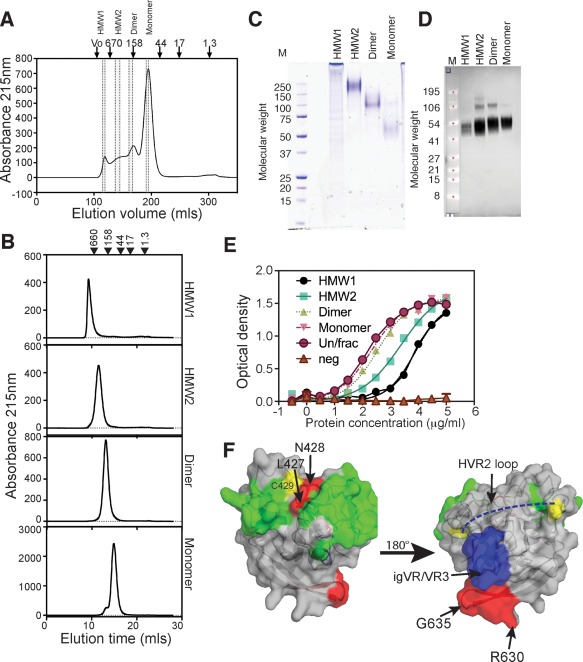
SEC purification and characterization of Δ123 species. (A) SEC profile of Δ123 using Superdex 200 showing areas of the profile that were pooled to generate HMW1, HMW2, dimer, and monomer species (area between dotted lines). The peak elution positions of standard proteins in kDa are shown above the chromatogram. (B) SEC profiles of individual purified species. (C) Nonreducing SDS‐PAGE and Coomassie blue staining of purified proteins (3 μg). Markers are shown on the left (kDa). (D) Western blotting of reduced proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membrane and detected with anti‐His antibody and scanned on an Odyssey imager. Markers are shown on the left (kDa). (E) Ability of proteins to directly bind dimeric CD81‐LEL. No binding was observed to the F186S CD81‐LEL mutant that abrogates E2‐CD81 interactions (neg). (F) Placement of residues that are occluded on the core domain of E2 (derived from Table 1 and Supporting Fig. S4). Red = residues that are occluded in HMW1. Blue surface = igVR/VR3 region. Dashed blue line is the putative location of HVR2. Yellow = Cys residues. Green = residues involved in binding CD81. On the left is the neutralizing face of E2 and on the right is the non‐neutralizing face of E2. N‐linked glycans are not shown. Arg630‐Gly635 is shown in red.
