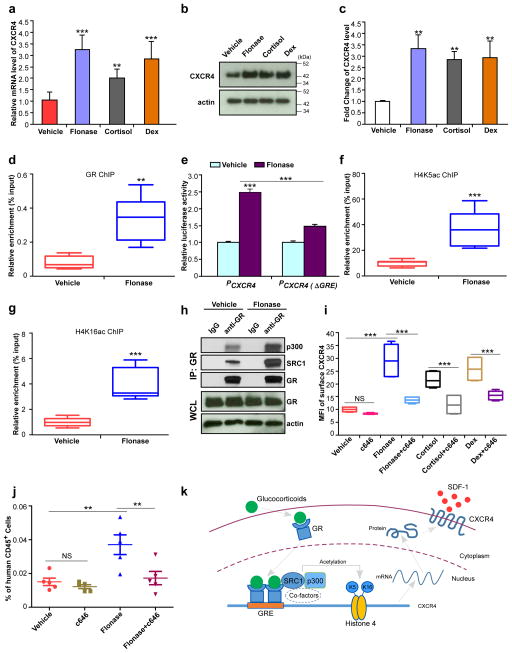
Figure 2. Glucocorticoids enhance H4K5 and H4K16 acetylation associated with the CXCR4 promoter, facilitate expression of CXCR4 and promote homing of human CB CD34+ cells.
(a) CXCR4 mRNA levels in Flonase, cortisol or Dex treated human CB CD34+ cells, relative to vehicle-treated cells, as assessed by quantitative realtime-PCR. Data pooled from three independent experiments are shown (n=9 replicates per group, one-way ANOVA).
(b,c) Total CXCR4 protein levels in Flonase, cortisol or Dex treated human CB CD34+ cells, relative to vehicle-treated cells, as assessed by western blotting. A representative blot is shown in b, and quantification of CXCR4 protein levels from three independent western blot assays is shown in c (n=3 experiments, one-way ANOVA). Actin was used as a loading control. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 4a.
(d) GR levels at the CXCR4 promoter in vehicle or Flonase treated human CB CD34+ cells, as assessed by a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. Data pooled from two independent experiments are shown (n=6 replicates per group).
(e) Promoter activities of the full length CXCR4 promoter (PCXCR4) and a glucocorticoid response element (GRE) defective form of the CXCR4 promoter (PCXCR4 (ΔGRE)) treated by vehicle or Flonase, as determined by a dual-luciferase reporter assay system. The relative luciferase activity of vehicle treated full length CXCR4 promoter group was set to 1 (n=3 replicates per group, one-way ANOVA). Representative data from three independent experiments are shown.
(f,g) Acetylated H4K5 (H4K5ac, f) and H4K16 (H4K16ac, g) levels at the CXCR4 promoter in vehicle or Flonase treated human CB CD34+ cells, as assessed by a ChIP assay. Data pooled from two independent experiments are shown (n=8 replicates per group).
(h) Levels of SRC1 and p300 that are co-immunoprecipitated with receptor GR in vehicle or Flonase treated human CB CD34+ cells. Extracts of treated cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-GR antibody and the resulting precipitates were analyzed by western blot. GR and actin in the whole cell lysate (WCL) serve loading controls. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 4b.
(i) Mean fluorescence intensity of surface CXCR4 in vehicle, c646 (30 μM), Flonase (10 nM), Flonase+c646, cortisol (1μM), cortisol+c646, Dex (100 nM), or Dex+c646 treated human CB CD34+ cells, as assessed by flow cytometry. Data pooled from two independent experiments are shown (n=6 cultures per group, one-way ANOVA).
(j) The percentage of human CD45+ cells in the bone marrow of NSG mice 24 h after transplantion with 500,000 CB CD34+ cells that had been treated with vehicle, c646 (30 μM), Flonase (10 nM) or Flonase+c646. (n=5 mice per group, one-way ANOVA). Data are shown as dot plots (mean±s.e.m.) in j, or as box-and-whisker plots (the lines indicate median values, the whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values, the boxes indicate interquartile range) in d, f, g and i. NS, not significant. **p<0.01. ***p<0.001.
(k) Model for the role of glucocorticoids in regulating CXCR4 expression in human HSC/HPCs. Glucocorticoid binding to GR in the cytoplasm results in GR activation, translocation to the nucleus and dimerization. The GR homodimer recognizes and binds to a GRE in CXCR4 promoter. Activated GR recruits SRC1, p300 and other co-factors with histone acetyltransferase activity to enhance acetylation of histone 4 on lysine 5 and lysine 16. Acetylation of histone 4 facilitates chromatin remodeling and promotes expression of CXCR4, and thus enhances HSC/HPC homing and engraftment.