FIGURE 6.
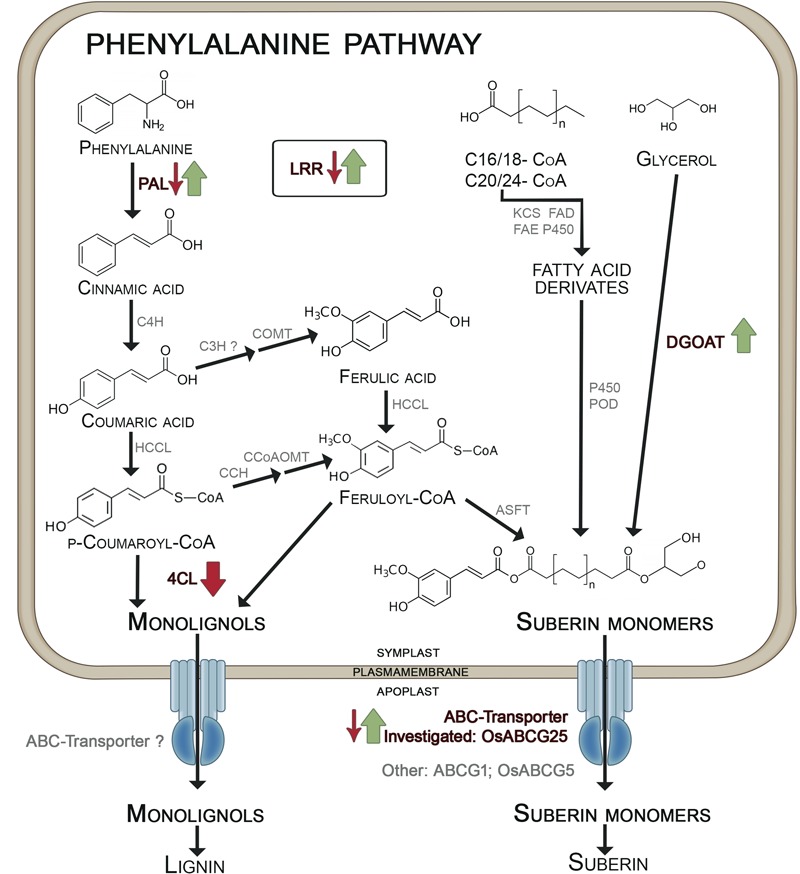
Differential expression of genes involved in exodermal CB development in mutants of OsABCG25. KO mutant: small arrows; OE mutant: big arrows. Phenylalanine-ammonia-lyase (PAL) catalyzes the formation of cinnamic acid which is metabolized by cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H) to coumaric acid. Ferulic acid is built by coumaroyl-CoA-3-hydroxylase (C3H) and caffeic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT). Hydroxycinnamate-CoA-ligase (HCCL) catalyzes the formation of coumaryl-CoA and feruloyl-CoA which are converted to monolignols by 4-coumarate ligase (4CL) (Zhong et al., 1998; Eckardt, 2002). From coumaryl-CoA also feruloyl-CoA is generated by p-coumaroyl CoA 3-Hydroxylase (CCH) and caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CcoAOMT) which is bound to suberin monomers by aliphatic suberin feruloyl transferase (ASFT). The aliphatic components of suberin monomers originate from fatty acid derivates and glycerol, which is incorporated by diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase (DGOT) (Franke et al., 2005; Franke and Schreiber, 2007; Li-Beisson et al., 2013). Both, monolignols and suberin monomers are transported by ABC-transporter from the symplast into the apoplast. We suggested that the investigated OsABCG25 transports suberin monomers. Other suberin transporters are ABCG1 (Landgraf et al., 2014) and OsABCG5 (Shiono et al., 2014). Further proteins are: CCH, p-coumaroyl CoA 3-hydroxylase; FAD, fatty acid desaturase; FAE, fatty acid elongase; KCS, β-ketoacyl-Coa synthase; LRR, leucine-rich repeat family protein; P450, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; POD, peroxidase. Arrows indicate significant regulation in KO/OE mutants vs. +WT/-WT (p-value > 0.01), green stands for upregulation, red stands for downregulation. The scheme based on Eckardt (2002) and Franke and Schreiber (2007).
