Fig. (1).
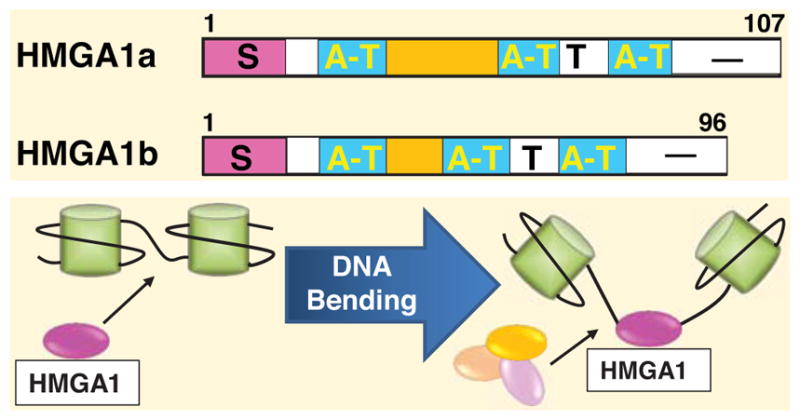
HMGA1a and HMGA1b protein isoforms are depicted with the serine (S) and threonine (T)-rich regions, AT-hook DNA binding domains (AT), and the acidic carboxyl terminal (−) region (top). HMGA1 functions as an architectural transcription factor that bends chromatin to enable binding of transcriptional complexes (bottom).
