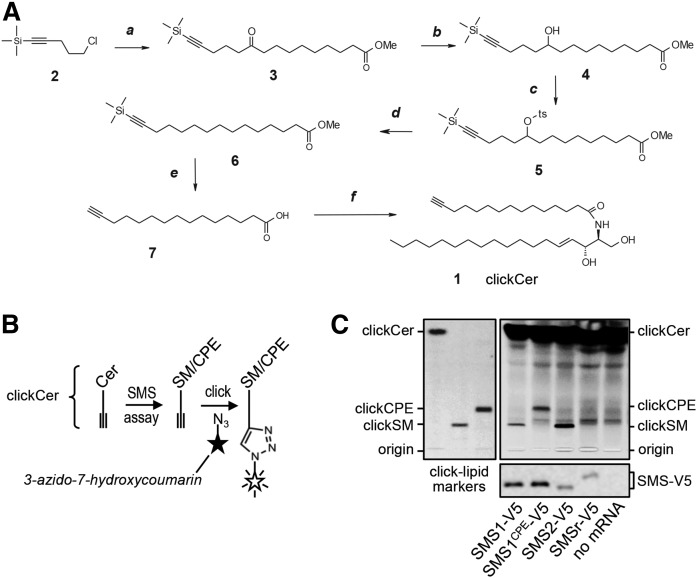
Fig. 3.
Tracing catalytic activity of cell-free-produced SMS enzymes by click chemistry. A: A clickable ceramide analog, clickCer (1), was synthesized by condensation of D-erythro-sphingosine and a C15-fatty acid carrying a terminal alkyne group (7). The latter was synthesized in five steps, as detailed in the Materials and Methods. Reagents and conditions: a, Mg, Et2O, C11H19O3Cl, room temperature; b, NaBH4, methanol-water), room temperature; c, TsCl, Et3N, DMAP, room temperature; d, NaBH4, DMSO, 75°C; e, KOH, methanol, 50°C; f, sphingosine, EDCI, HOBT, room temperature. B: Schematic outline of the click-chemistry-based SMS assay. ClickCer was incorporated as SMS substrate in liposomes present during the cell-free translation of SMS-V5 mRNA. After lipid extraction the alkyne moiety was click-reacted with the fluorogenic dye, 3-azido-7-hydroxycoumarin, to yield fluorescently labeled lipids. The scheme was adapted from (29). C: V5-tagged SMS1, SMS1CPE, SMS2, and SMSr were produced cell-free in the presence of liposomes containing 2 mol% clickCer. After lipid extraction, SMS reaction products were click-reacted with 3-azido-7-hydroxycoumarin, separated by TLC, and analyzed by fluorescence detection. SMS expression was verified by immunoblotting using anti-V5 antibody (bottom). Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. Boldface numbers correspond to intermediates of clickCer synthesis described in Materials and Methods.