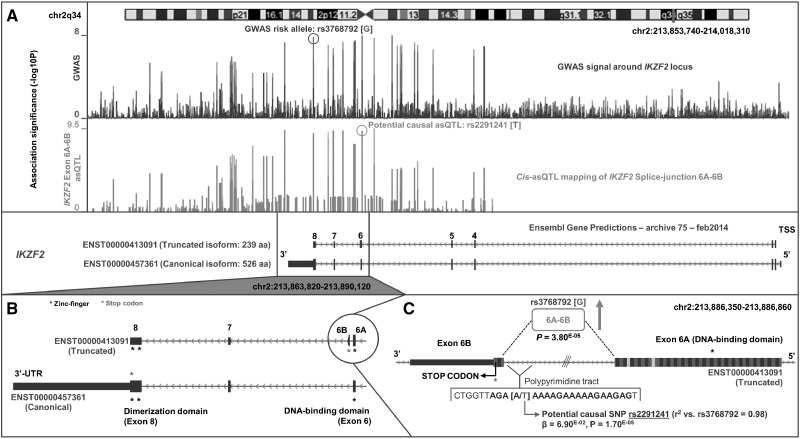
Figure 4.
Novel eGene IKZF2 and potential causal mechanism using splice-junction quantification. asQTL analysis of rs3768792 against splice-junction quantifications identifies IKZF2 as a candidate-causal eGene with risk variant [G] causing upregulation of the exon 6A–exon 6B junction that is unique to truncated isoform ENST00000413091. A) GWAS association signal across the IKZF2 locus (chr2q34), tagged by rs3768792 localised in the 3′-UTR of IKZF2. asQTL association signal of rs3768792 against splice-junction quantification of exon 6A–exon 6B shows significance and colocalisation with the GWAS signal. B) The exon 6A–exon 6B junction is unique to truncated isoform ENST00000413091. Exon 6B harbours a premature stop-codon and therefore is not translated into the full-length protein that contains the dimerization domains in exon 8. C) Close-up of the exon 6A–exon 6B junction and association (P = 3.80 × 10−05) with GWAS SNP rs3768792. A potential causal asQTL in near-perfect LD was identified that is located within the polypyrimidine tract of the junction and may induce splicing (rs2291241, P = 1.70 × 10−05).