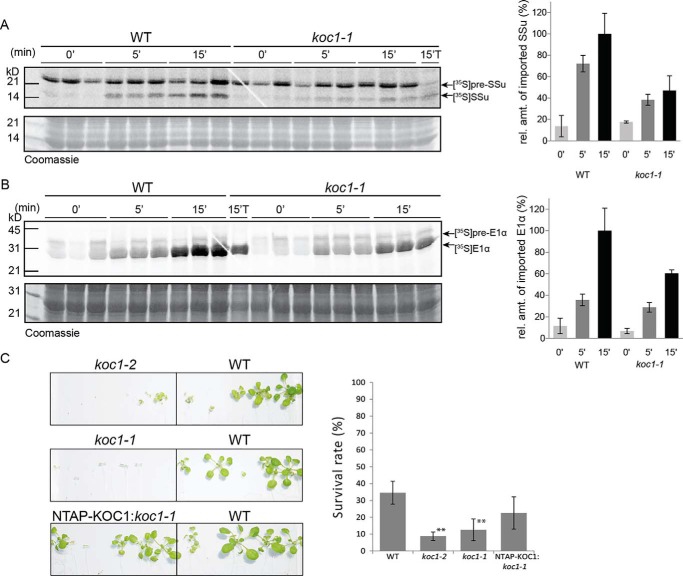
Figure 6.
Requirement of KOC1 for efficient chloroplast protein import and de-etiolation. A and B, isolated chloroplasts from koc1-1 and Col-0 (WT) plants were incubated with [35S]Met-labeled preproteins of pSSu in A and E1-α in B. The preproteins were incubated with chloroplasts, and import was allowed to proceed for 0, 5, and 15 min (0′, 5′, and 15′); one sample was treated with thermolysin after 15 min (15′T). Proteins from chloroplasts were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by phosphorimaging analysis. The graphs show the quantification of the bands corresponding to imported mature SSu and E1α at 0, 5, and 15 min averaged over three technical replicates. The amount of mature protein imported into WT chloroplasts at 15 min was arbitrarily set to 100%. The qualitatively similar results were obtained in five independent experiments. C, images of surviving koc1-2, koc1-1, WT, and NTAP-KOC1:koc1-1 plants upon exposure to long-day conditions for 2 weeks after etiolation for 6 days in dark. The germination and survival rates were calculated. The germination rate was around 100% for all genotypes. The survival rates were as follows: WT, 34.6%; NTAP-KOC1:koc1-1, 22.5%; koc1-2, 8.8%; and koc1-1, 12.5% (Student's t test: **, p value <0.01; *, p value <0.05 (n = 80 for koc1-1 and koc1-2; n = 240 for WT)). Error bars represent S.D. This experiment was repeated three times with comparable results. rel. amt., relative amount.