Figure 5.
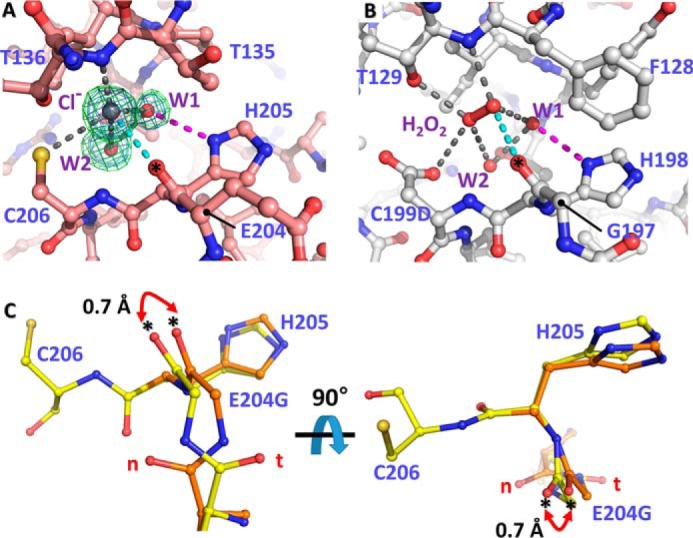
Structural variation of VvOxyR2 His-205 at the H2O2 and water binding sites near the peroxidatic cysteine residue. The putative chloride ion in VvOxyR2 (A) and the H2O2 molecule in P. aeruginosa OxyR (B; PDB code 4X6G) are bound near the peroxidatic cysteine (C206) or the mutated aspartic acid (C199D) residue. The polar interactions involved in binding the chloride ion (gray ball) or H2O2 (red ball and stick) are indicated by dotted lines. The bound water molecules (W1 and W2) are indicated by red balls. The 2Fo − Fc (blue mesh) and Fo − Fc (green mesh) omit maps of chloride ion and water molecules are contoured at 1.0 σ and 3.0 σ, respectively. C, two orthogonal views of the SO4-free high-resolution structure of VvOxyR2 E204G variant. The alternative residues are presented by yellow or orange ball-and-stick representations. The difference points in dual conformation are indicated by red dihedral arrows. t and n letters in red indicate the typical conformation observed in the most OxyR proteins and the noncanonical conformation only observed in the wild-type VvOxyR2, respectively. *, carbonyl atom between Glu-204 (or Gly-204) and His-205.
