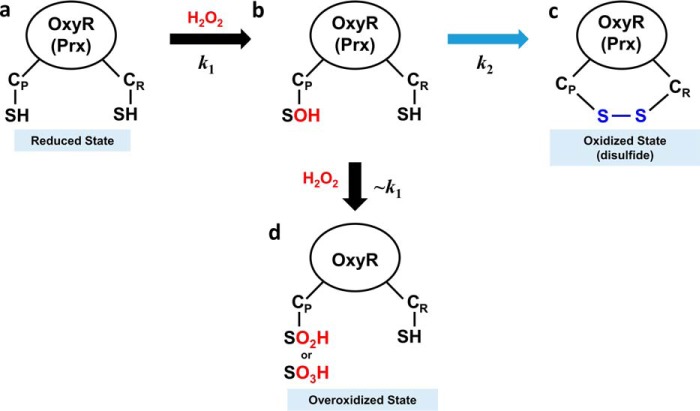
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of an oxidation mechanism for OxyR and Prx protein. a, the OxyR or Prx in the reduced state has two free thiols at the CP and CR. b, H2O2 rapidly reacts with CP, resulting in CP-SOH at the second-order reaction rate constant of k1. c, CP-SOH then forms a disulfide bond with CR, resulting in the oxidized state with a disulfide bond at the reaction rate constant of k2. d, in an alternative to c, CP-SOH is further oxidized by additional H2O2, resulting in the overoxidized state with CP-SO2H or CP-SO3H. Due to the structural similarity with OxyR in the reduced state, the second-order reaction rate constant would be close to k1 (∼k1).