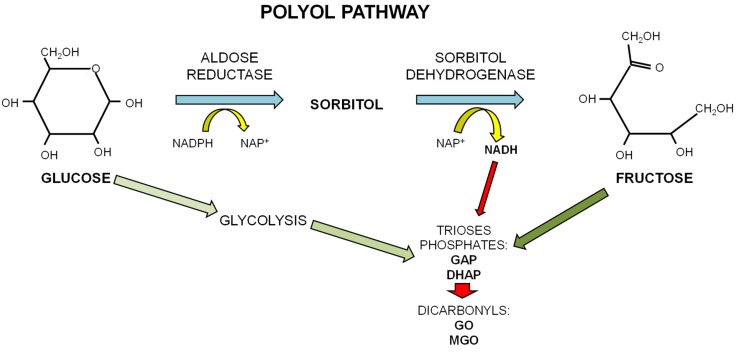
Scheme 2.
The polyol pathway. In conditions of excess of glucose, as occurring in diabetes, glucose undertakes the polyol pathway to be converted to fructose through the consecutive action of aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase. This alternative pathway for the metabolism of glucose leads to the increase in fructose levels in tissues of diabetic patients and of the NADH/NAD+ ratio that contrasts GAP-dehydrogenase activity leading to accumulation of the triose phosphates GAP and DHAP, precursors of the dicarbonyls compounds glyoxal (GO) and methylglyoxal (MGO).