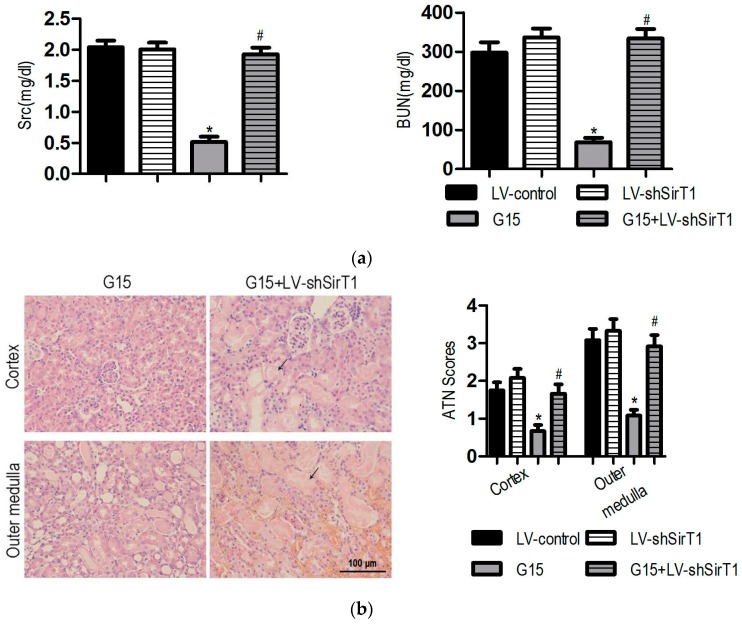
Figure 6.
SIRT1 depletion abrogates the protective effect of genistein on renal function and histology in I/R-induced injury. In the LV-control, mice were injected with lentivirus carrying scrambled shRNA and pre-treated with the same volume of vehicle; in the LV-shSIRT1 group, mice were injected with lentivirus carrying SIRT1 shRNA; in the G15 group, mice were injected with lentivirus carrying scrambled shRNA and were pre-treated with 15 mg/kg genistein; in the LV-shSIRT1 + G15 group, mice were injected with lentivirus carrying SIRT1 shRNA and were pre-treated with 15 mg/kg genistein. Ischemia was induced in all of the groups. The mice were decapitated after 24 h of reperfusion for further analysis. The data were expressed as the mean ± SEM; n = 6; * p < 0.05 vs. Sham; # p < 0.05 vs. I/R. The Scr (a, left) levels and BUN (a, right) levels were examined 24 h after reperfusion. (b, left) Representative images of the cortex and outer medulla from G15 and G15 + LV-shSIRT1 groups stained with H&E. Original magnification, 400×. The black arrows indicate the areas of I/R-induced tissue damages. (b, right) Semi-quantitative assessment of the lesion was performed by a pathologist in a blinded manner according to the ATN-scoring system. Each tubular segment visible in the cortex and outer medulla was evaluated.