Figure 1. Behavioral task and task-evoked pupil responses.
(A) Yes-no contrast detection task. Top: schematic sequence of events during a signal+noise trial. Subjects reported the presence or absence of a faint grating signal superimposed onto dynamic noise. Bottom left: the signal, if present, was oriented clockwise or counter clockwise on different blocks (known to the subject beforehand). Signal contrast is high for illustration only. Bottom right: trial types. (B) Quantifying task-evoked pupillary response (TPR) amplitude. Top: mean TPR time course of an example subject. Green box, interval for averaging TPR values on single trials. Bottom: trials were pooled into three bins of TPR amplitudes (lowest/highest 40% and intermediate 20%). (C) TPR time course for the three bins. (D) Mean beta weights of transient (cue, choice) and sustained input components under low vs. high TPR, estimated with a general linear model (see Materials and methods; Figure 1—figure supplement 1A,B), separately for low and high TPR trials. Panels C, D: group average (N = 14); shading, s.e.m.; data points, individual subjects; stats, permutation test.
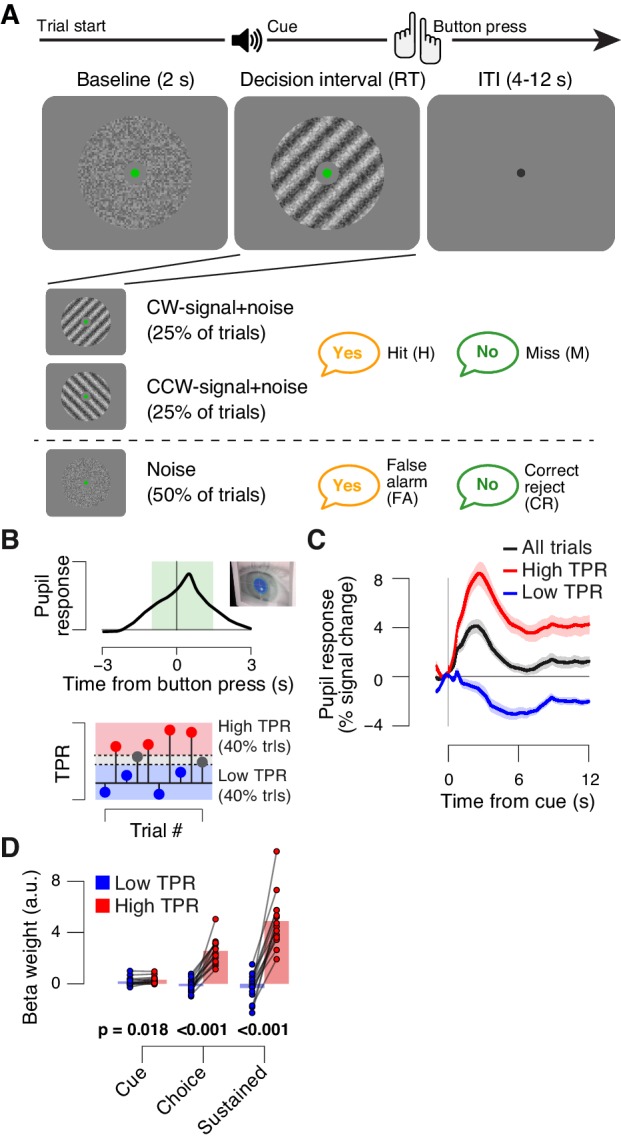
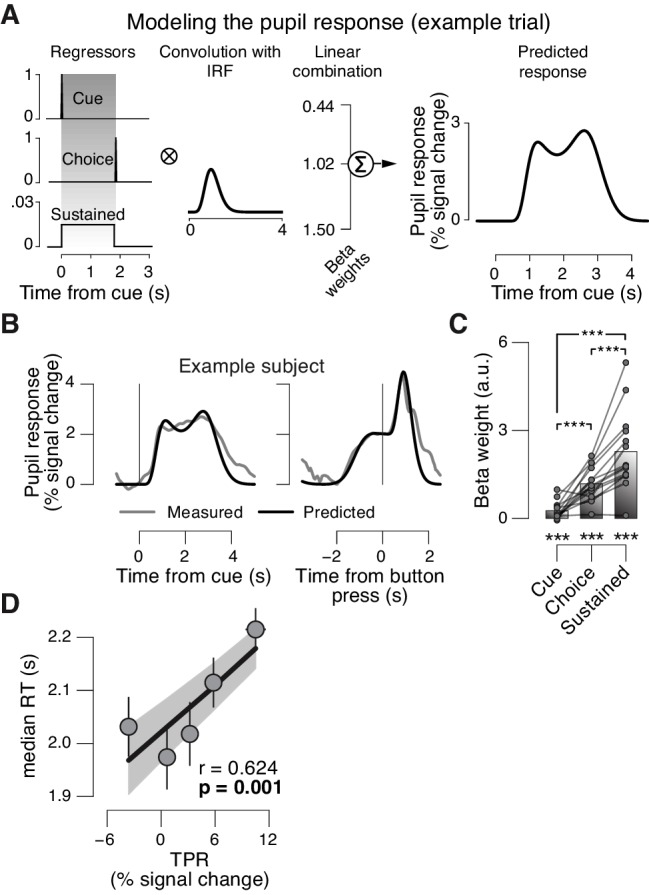
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Linear modeling of TPR.