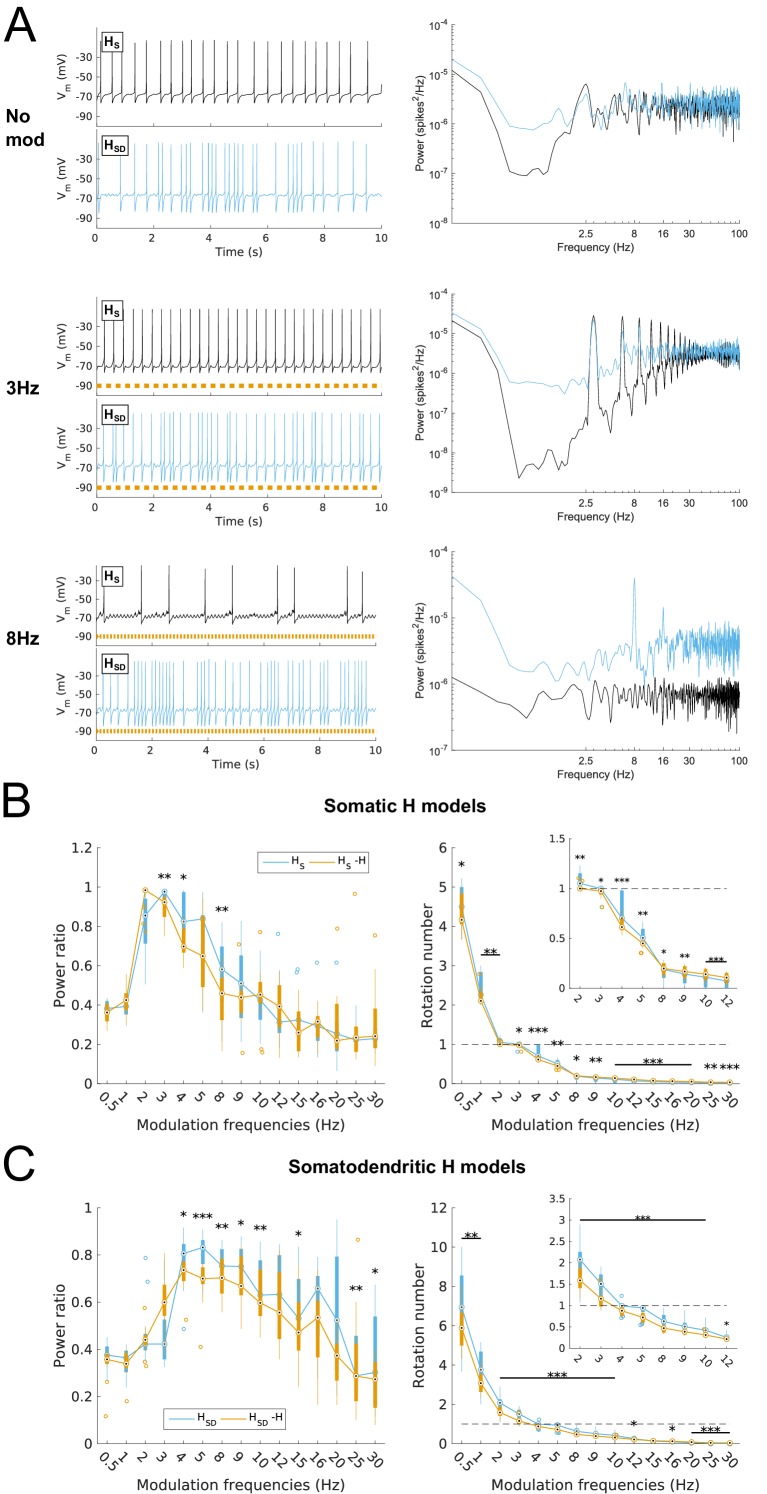
Figure 2. Effects of dendritic H distribution and H block on recruitment of O-LM model spiking in response to modulated somatodendritic inhibitory input.
(A) Somatic Vm traces for example somatic H model (HS, black) and somatodendritic H model (HSD, blue) under various modulation conditions (top – no modulation; middle – 3 Hz modulation; bottom – 8 Hz modulation). With modulated inputs, orange bars at bottom denote phase of peak modulation at the specified frequency (see Materials and methods). Power spectrum density (PSD) plots shown to the right of each output trace. (B, C) Power ratios (left) and rotation numbers (right) under different modulation frequencies for models with somatic H (B) and somatodendritic H (C) in control and H blocked (‘-H’) conditions. Insets in rotation number plots show zoomed portion in the theta range (2–12 Hz). Statistical test used was repeated measures ANOVA for the populations of HS and HSD models between all modulation frequencies crossed with H block condition (power ratios HS: F(1,15) = 2.23, p=0.013, n = 16; HSD: F(1,15) = 2.89, p=0.017, n = 16; rotation numbers HS: F(1,15) = 27.94, p<0.001, n = 16; HSD: F(1,15) = 10.35, p=0.006, n = 16; Huynd-Feldt correction reported for all tests). Boxplot annotations as per Figure 1G legend.