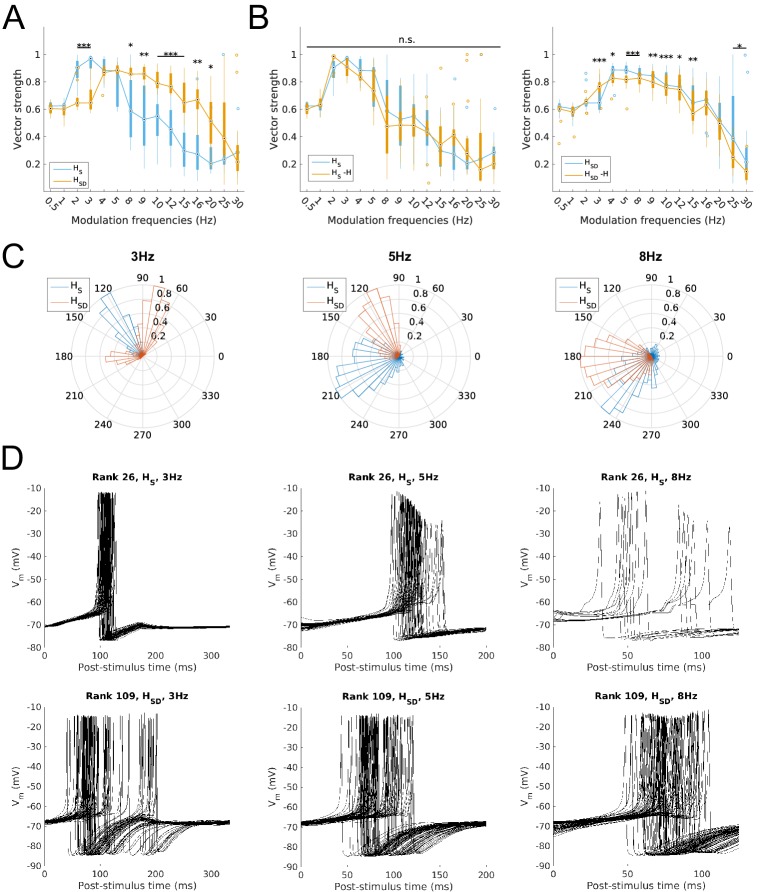
Figure 3. Firing precision and phase of models with modulated somatodendritic inputs.
(A) Firing precision (vector strength) across models with somatic H (blue) and somatodendritic H (orange) in control (without H block), across all modulation frequencies (F(1,15) = 9.378, p<0.001, n = 16; Huynd-Feldt correction). Boxplot annotations as per Figure 1G legend. (B) Vector strength across models with somatic H (HS, left) and somatodendritic H (HSD, right), in control (blue) and with H blocked (orange), across all modulation frequencies. Statistical test used was two-way repeated measures ANOVA for the populations of HS and HSD models between all modulation frequencies crossed with H block condition (HS: F(1,15) = 1.682, p=0.13, n = 16; HSD: F(1,15) = 4.45, p=0.009, n = 16; Huynd-Feldt correction reported for both tests). Boxplot annotations as per Figure 1G legend. (C) Firing phase histograms for models with somatic H (blue) and somatodendritic H (orange) for modulation frequencies of 3 Hz (left), 5 Hz (middle), and 8 Hz (right). (D) Overlay of Vm traces of all spikes for a sample somatic H model (top row) and somatodendritic H model (bottom row), cut and aligned with respect to the time of release from inhibition at 3 Hz (left), 5 Hz (middle), and 8 Hz (right).