Figure 1.
hURI-tetOFFhep Mice Display HPC Signatures in Early Hepatocarcinogenesis Stages Correlating with Aggressive Human HCC
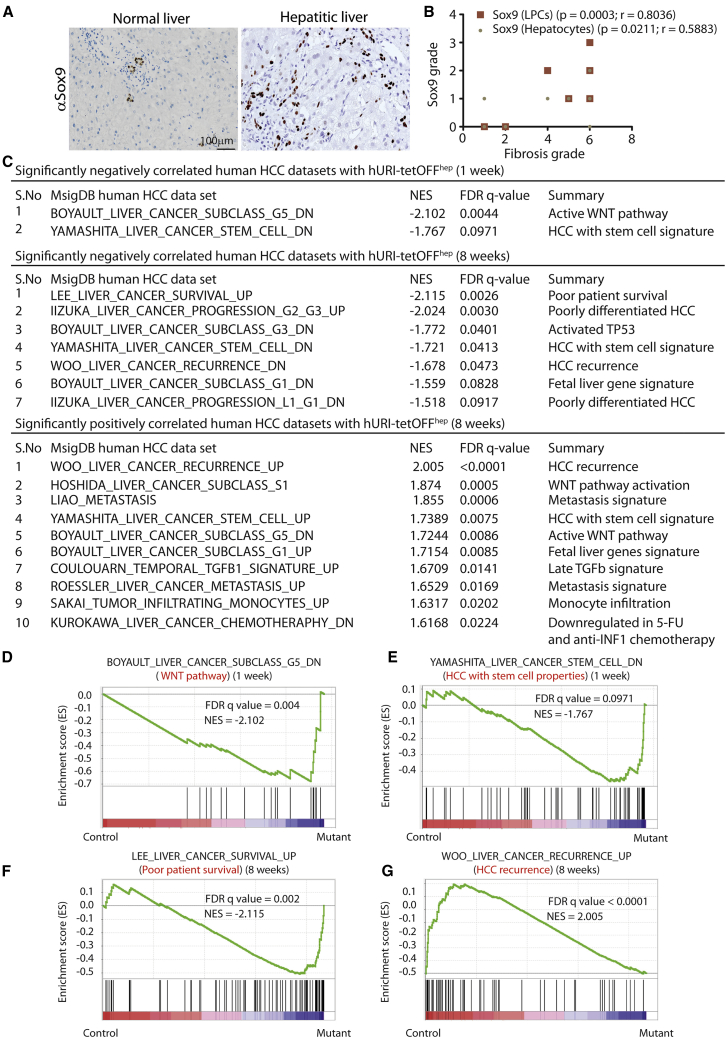
(A) Representative images of Sox9 immunohistochemistry (IHC) in human hepatitis samples. Sox9 expression was evaluated in the liver progenitor cells (LPCs) and hepatocytes (n = 15).
(B) Graph representing the correlation between fibrosis grade and Sox9 expression in human hepatitis samples (n = 15).
(C) Table summarizing the most significantly enriched human HCC gene sets in 1- or 8-week-old hURI-tetOFFhep mice.
(D) GSEA of human HCC WNT pathway and 1-week-old hURI-tetOFFhep mice protein signature.
(E) GSEA of human HCC stem cell properties and 1-week-old hURI-tetOFFhep mice protein signature.
(F) GSEA of human HCC poor patient survival and 8-week-old hURI-tetOFFhep mice protein signature.
(G) GSEA of human HCC recurrence and 8-week-old hURI-tetOFFhep mice protein signature. All protein signature datasets obtained for hURI-tetOFFhep mice were previously described and achieved by iTRAQ (Tummala et al., 2014).
Normalized enrichment score (NES) and false discovery rate (FDR) q-values are indicated in each graph. Scale bar represents 100 μm.