Figure 1.
CB Stem Cells Contribute to Angiogenesis in Addition to Neurogenesis under Hypoxia
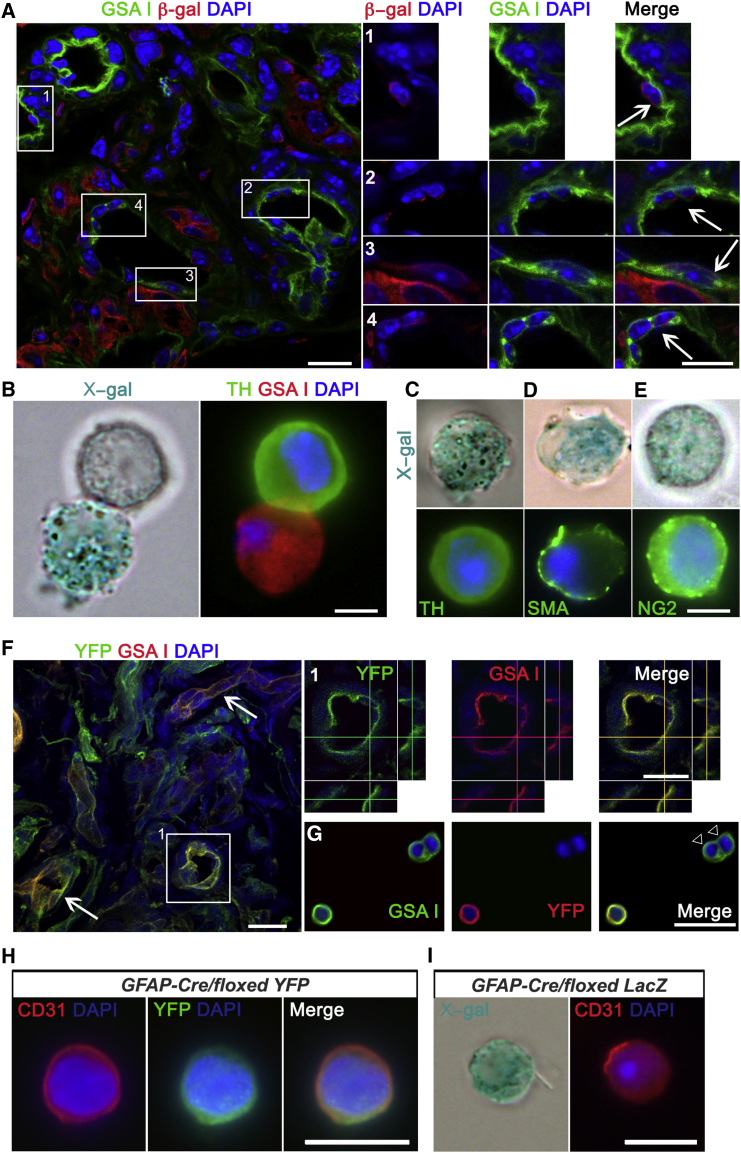
(A) Z stack projection picture obtained by confocal microscopy from a CB section of a hypoxic GFAP-cre/floxed LacZ mouse, immunostained with an antibody against β-galactosidase (red) and stained with the endothelial marker GSA I (green). ECs derived from GFAP+ type II cells are shown in the enlargements of the boxed areas (arrows). Scale bars, 10 μm. Confocal pictures were taken in sections from two animals per group.
(B–E) Examples of X-gal+ cells dispersed from the CB of hypoxic GFAP-cre/floxed LacZ mice. The pictures illustrate the appearance of X-gal+ ECs (GSA I+, B), glomus cells (TH+, C), smooth muscle cells (SMA+, D), and pericytes (NG2+, E). Scale bars, 5 μm. n = 3 independent experiments.
(F) Fluorescence confocal microscopy pictures of CB sections from hypoxic GFAP-cre/floxed YFP mouse stained with anti-YFP antibody (green) and rodhamine-conjugated GSA I lectin. Arrows point to double-positive vessels. A higher magnification of the boxed region depicted in (F), showing z axis projection views, is shown in (1). Scale bars, 25 μm. n = 3 animals per experimental group.
(G) Picture of ex vivo hypoxic CB preparation stained with GSA I (green) and immunolabeled with an antibody against YFP reporter protein (red). Note the presence of GSA I positive ECs, negative for the reporter protein (white arrowheads). Scale bar, 25 μm.
(H and I) Examples of GFAP+ cell-derived CD31+ ECs, found in CB cell dispersions from both GFAP-cre/floxed YFP (H) and GFAP-cre/floxed LacZ (I) mice. Scale bars, 20 μm.
See also Figures S1 and S2.