Fig. 4.
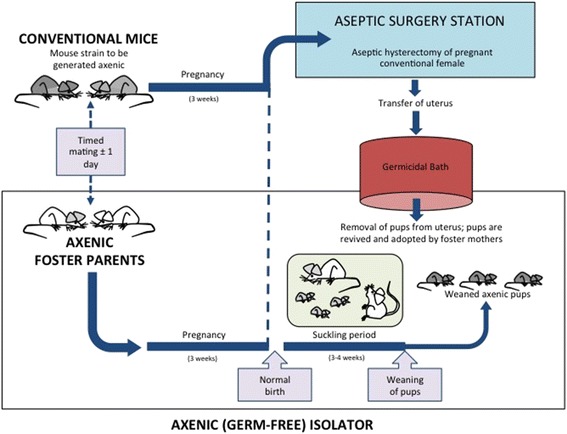
Schematic representation of the generation of axenic rodents by aseptic hysterectomy. In rodents, germ-free offspring are derived by aseptic hysterectomy. Germ-free foster mothers housed in a sterile isolator are time-mated to become pregnant in synchrony with holoxenic (conventional) females. Breeding pairs are mated on such a schedule that the aseptic hysterectomy of the donor mother can be performed a few hours before her scheduled pupping and a few hours after the foster mother gives birth. To perform the hysterectomy, donor females are euthanized, and the uterus is harvested and clamped, aseptically introduced into a germicidal bath, and then transferred into the sterile isolator where the foster mothers reside. The pups are then revived and placed under the care of the foster mother [123–125]. If there are no germ-free foster mothers available, then pups are hand-raised using sterile formula. Figure adapted from Hedrich and Hardy [125]
