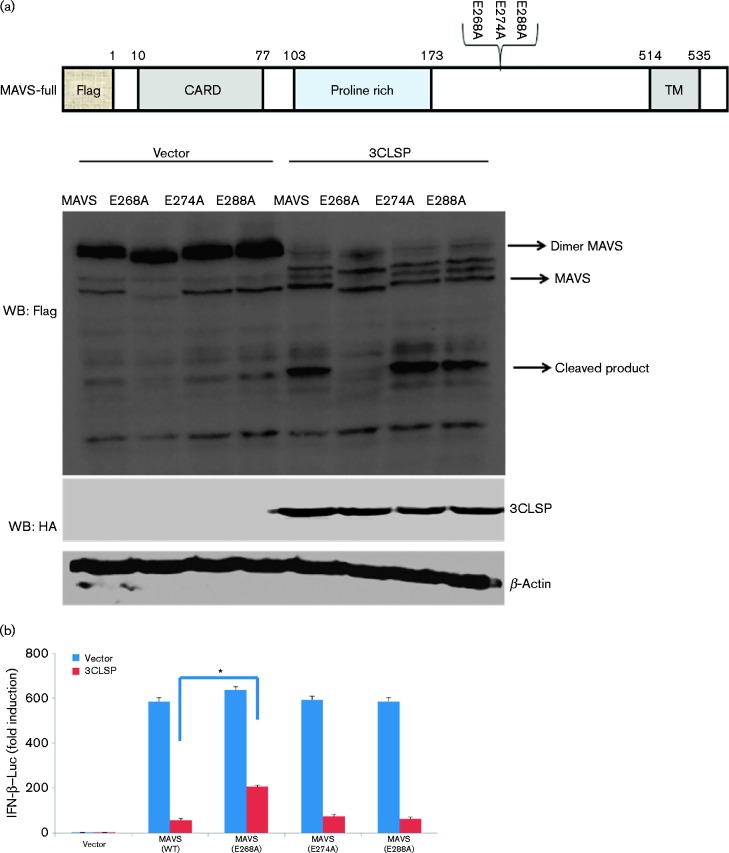
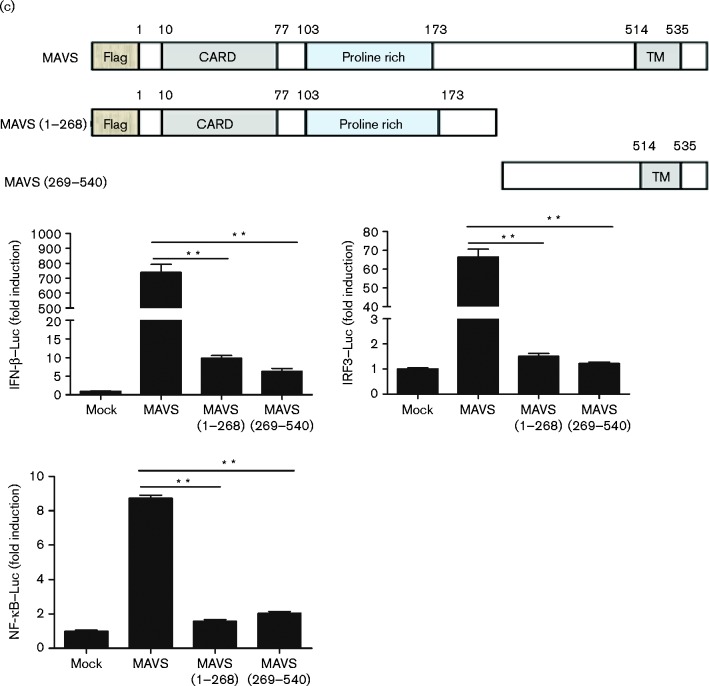
Fig. 6.
3CLSP-mediated MAVS cleavage is involved in the inhibition of type I IFN induction. (a) Schematic representation of WT MAVS and its derivatives. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with Flag-tagged WT MAVS or MAVS mutants (E268A, E274A and E288A) along with 3CLSP or an empty vector. These cells were lysed at 32 h post-transfection and analysed by Western blotting (WB). (b) HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with IFN-β–Luc, the pRL-TK plasmid and a plasmid encoding 3CLSP (0.3 μg) together with the empty vector, MAVS or MAVS (E268A) expression vector (0.3 μg). Luciferase activity was examined at 32 h post-transfection. The MAVS E268A mutant was significantly different from WT MAVS (*P < 0.01). (c) MAVS or MAVS truncated mutants are shown. Complete MAVS contained the N-terminal CARD domain, proline-rich domain and C-terminal TM domain. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with the indicated reporter plasmid (0.1 μg), pRL-TK (0.1 μg) or the Flag-tagged MAVS expression plasmid (0.5 μg) along with a plasmid encoding Flag-tagged WT MAVS, 3CLSP-induced cleavage fragments of MAVS or an empty vector. **P < 0.01. Results are shown as means ± sd.