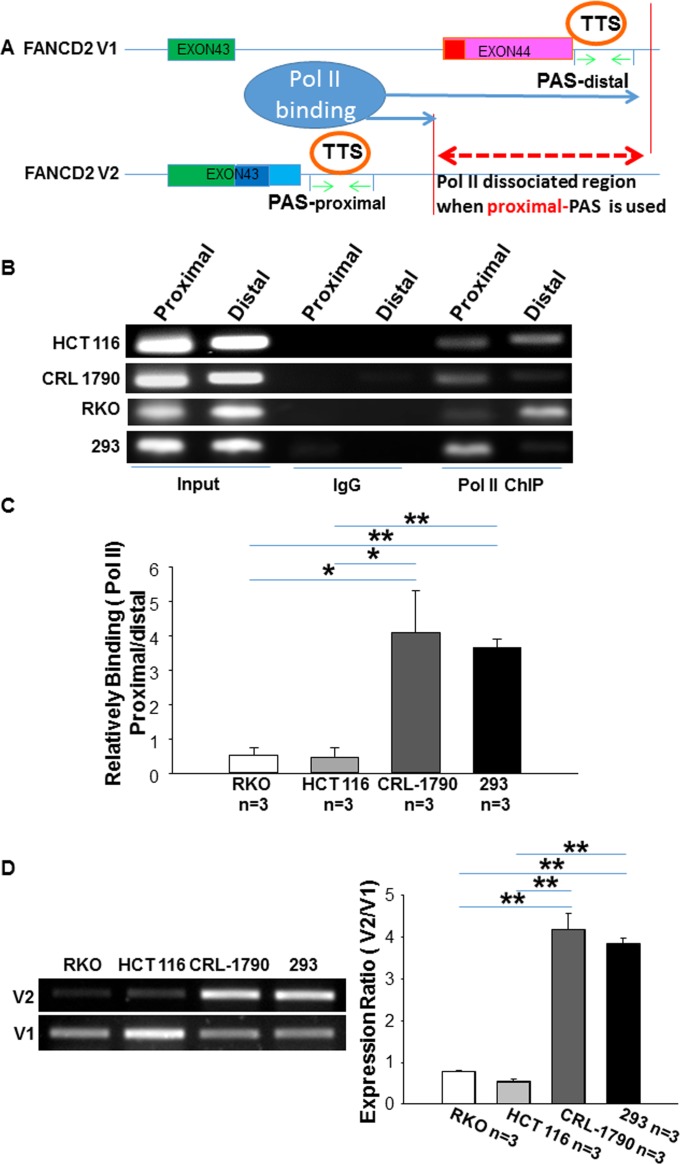
Figure 2. RNA polymerase II binds relatively more to the distal PAS region of FANCD2 gene in cancer cells as compared to the non-cancer cells.
(A) Alternative Transcription Termination Site (TTS) follows alternative PAS, and RNA pol II dissociates from DNA template at TTS and stops transcription [43], upon which DNA fragments after TTS can be distinguished by the binding capacity of pol II antibodies. As green arrowheads indicated, proximal or distal primer-bracketed regions pulled down by pol II antibodies are able to define the frequency of usage for proximal or distal PAS during the transcription. Therefore, the dash red line indicates the region where pol II is unable to binds when proximal-PAS is used. (B, C) Pol II antibodies pulled down relatively more DNA fragments located at the distal-PAS region in malignant cells (HCT116 or RKO) as compared to the non-malignant cells (CRL1790 or HEK293). t-test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (The bar-graph was plotted from Real-time qPCR.). (D) The V1 or V2 mRNA expression in these cells used for ChIP or RIP (next figure): V1 expression is relatively higher in non-malignant cells compared to malignant cells.