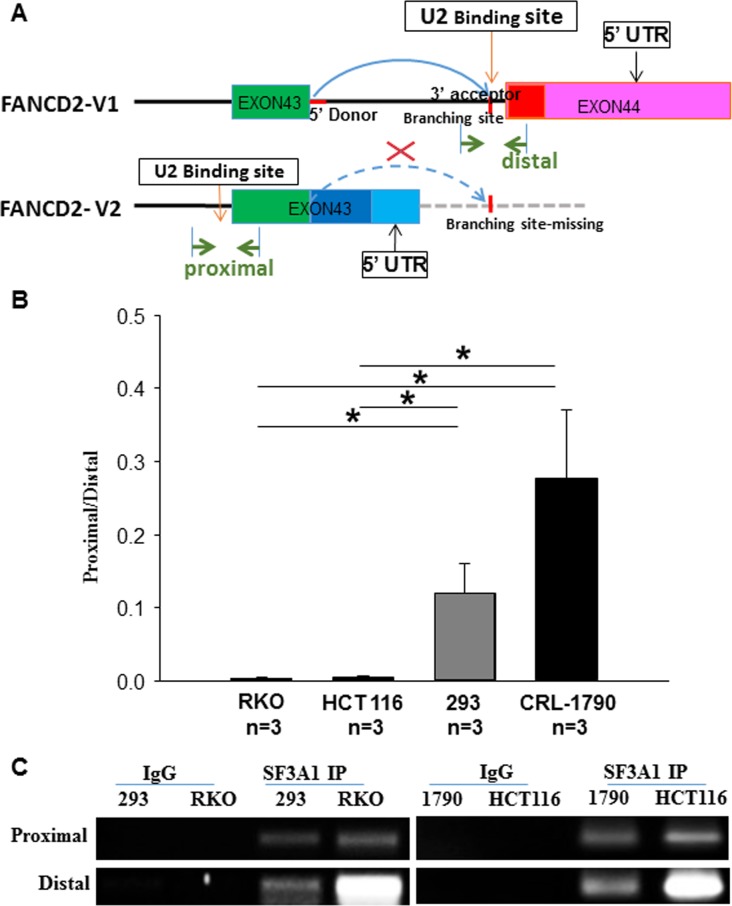
Figure 3. SF3A1 (the core component of U2 snRNP) RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) shows that U2 snRNP interacts more with the last intron of V1 transcript in cancer cells as compared to the non-cancer cells.
(A) Schematic representation of the pre-mRNA splicing outline for V1 and V2 variants: when the proximal PAS is used, the resulting V2 transcripts lacks the last intron (the curve dash blue line), shown in the V1 transcript. The RIP-PCR primers were designed upon the regions marked with green arrowheads (distal or proximal primers were called accordingly for detecting relevant RNA fragments). RT-qPCR was used to detect RNA fragments pulled down by antibodies targeting SF3A1 (a key component of U2 snRNP). (B) The RT-qPCR product ratio, reflecting the relatively binding capacity between SF3A1 and the last intron of V1 or V2: U2 snRNPs interact relatively more with the last intron of V1-transcript in cancer cells as compared to the non-cancer cells. t-test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (C) Agarose gel images of resolved RT-qPCR products: those images show a good quality of RIP and validate the size of anticipated PCR products.