Figure 3. Folate cycle is coupled with Methionine cycle.
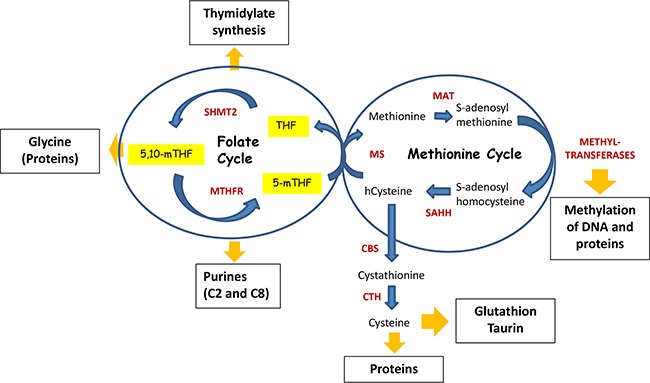
During Folate cycle MTHFR reduces 5,10-methyleneTHF to 5-methylTHF. Subsequently, 5-methylTHF donates its carbon group to convert homo-cysteine (hcystein) to methionine by methionine synthase (MS), hence initiating Methionine cycle. In turn, methionine is used by methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) to generate S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) – the principal donor of methyl groups for DNA and proteins methylation. Thus, SAM is used by different methyltransferases, resulting in S-adenosylhomocysteine after its demethylation. Finally, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) mediates deadenylation of S-adenosylhomocysteine to hcysteine, enclosing the methionine cycle. Homocysteine can be used by cystathionine synthase (CBS), which converts it to cystathionine. In turn, cystathionine is a substrate for cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH), which uses it for synthesis of cysteine. Cysteine is required for the synthesis of proteins as well as for generation of taurine and glutathione, the latter is one of the critical molecules for redox homeostasis.
