Figure 4. Major pathways of the nucleotide biosynthesis.
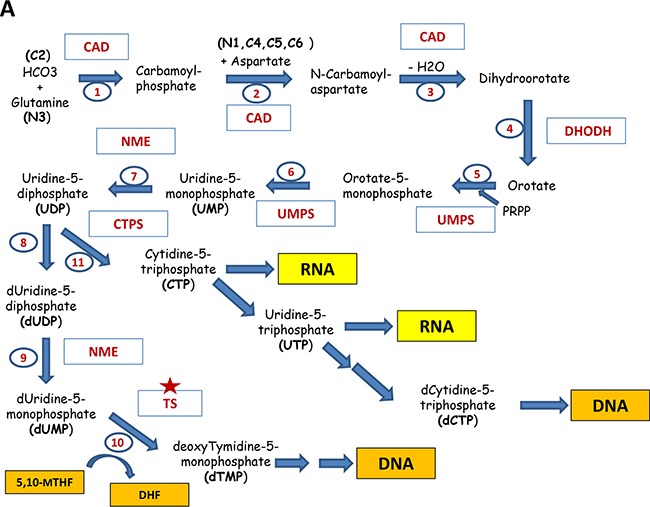
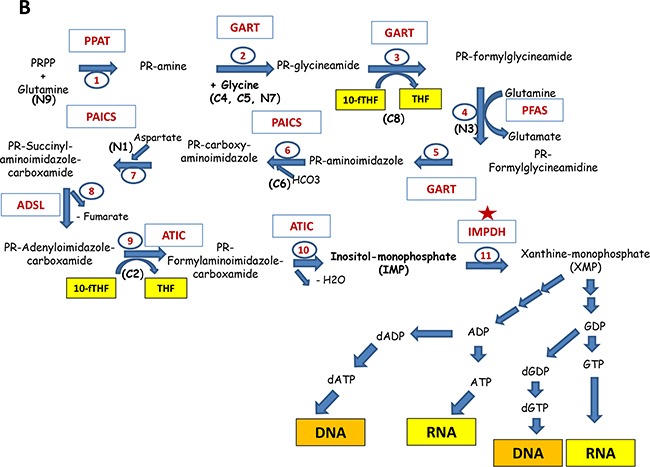
A. Shown are the reactions of the biosynthesis of pyrimidines: The participating enzymes are shown in red. The input compounds, intermediates and the resulting products are indicated (future positions of atoms in the nucleotide are indicated in brackets). Reactions are numbered in sequential order. Thus, reactions 1, 2 and 3 are catalyzed by tri-functional enzyme Carbamoyl Dehydrogenase (CAD); 4 – Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH);5 and 6 – bifunctional Uridine Monophosphate Synthetase (UMPS); 7,8,9 - Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase (NME); 10 - Thymidylate synthase (TS), 11 - CTP Synthase (CTPS). Red asterisks indicate the enzymes that are currently being explored as drug targets. Enzymes marked with orange asterisks are considered as potential drug targets. B. The biosynthesis of purines. Abbreviations are the same as in part A.
