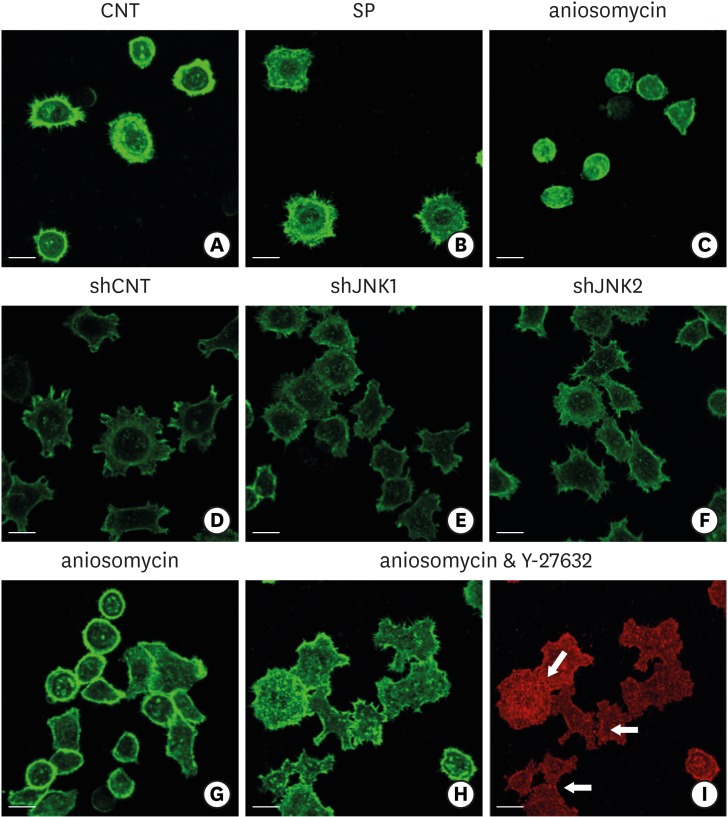
Figure 8.
Influence of JNK on the organization of F-actin during ECJ development. (A-C) The development of cortical actin was assessed using CLSM after treating the cells with SP (1 µM) (B), or anisomycin (20 ng/mL) (C) for 20 hours from the start of cell culture on the smooth substrate. CNT (A) indicates the control culture without treatments regulating JNK activity. F-actin was stained with FITC-phalloidin (bar=20 µm). (D-F) Cortical actin development was assessed using CLSM after HGKs infected with lentiviruses expressing shJNK1 (E) or shJNK2 (F) to selectively inhibit JNK1 or JNK2 were cultured for 8 hours on the rough substrate with low-nanometer dimensions (Ra=121.3±13.4 nm). Control cells (shCNT) (D) were cultured after transfection with scrambled shRNA. F-actin was stained with FITC-phalloidin (bar=20 µm). (G-I) Cortical actin development and ECJ development (arrows) were assessed using CLSM after treating the cells with anisomycin (20 ng/mL) (G) or co-treating the cells with anisomycin (20 ng/mL) and Y-27632 (20 µM) (H, I) for 20 hours from the start of cell culture on the smooth substrate. F-actin (green) was stained with FITC-phalloidin. ECJ development was followed by immunocytochemical staining for the expression level of E-cadherin (red) (bar=20 µm).
JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase, ECJ: E-cadherin junction, CNT: carbon nanotube, Ra: average roughness, SP: SP600125, CLSM: confocal laser-scanning microscopy, FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled, sh: small hairpin.