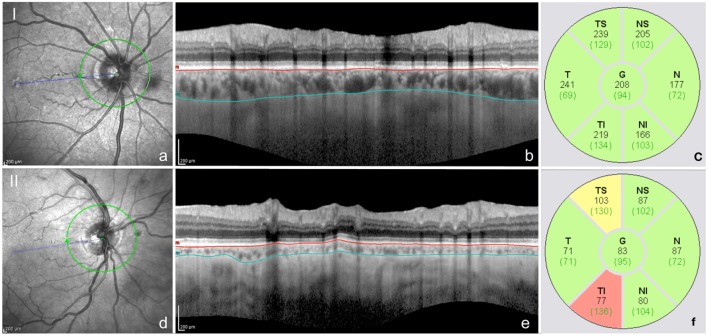
Figure 2.
Peripapillary choroidal thickness measurements obtained by peripapillary spectral domain-optical coherence tomography scans using the enhanced depth imaging mode (a,d). Images I and II correspond to the left eye of two different idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients, one after successful VP-shunting surgery (I) and another before VP-shunting surgery (II). The automatic detection of the internal limiting membrane and retinal nerve fiber layer were manually changed to delineate the external border of the retinal pigment epithelium (superior line) and the external limit of the choroid (inferior line), respectively (b,e). Automatic readings of the choroidal thickness were obtained in all quadrants (c,f). Choroidal thickness values are displayed in black and values of the normative database for retinal nerve fiber layer thickness evaluation of the Spectralis Heidelberg are displayed in brackets (c,f).