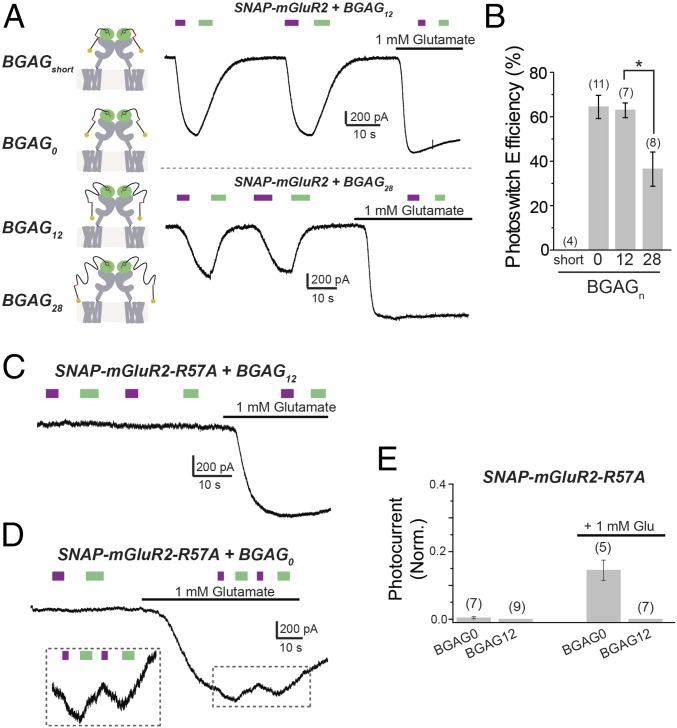
Fig. 2.
Mechanism of SNAG-mGluR2 photoswitching: BGAG length dependence, glutamate affinity, and subunit specificity. (A) Characterization of BGAG length dependence. BGAG variants of differential PEG linker lengths (depicted in cartoons; Left) were tested on SNAP-mGluR2. (A, Right) Representative traces showing photoactivation of SNAG-mGluR2 by BGAG12 (Top) or BGAG28 (Bottom). (B) Summary of photoswitch efficiency relative to saturating 1 mM glutamate for BGAG variants on SNAP-mGluR2. * indicates statistical significance (unpaired t test between BGAG12 and BGAG28, P = 0.004). (C and D) Reduction of glutamate affinity with the mutation R57A abolishes photoswitching of SNAG-mGluR2 in the absence of glutamate for both BGAG12 (C) and BGAG0 (D). (D, Inset) Photoswitching in the presence of 1 mM glutamate for BGAG0, indicating cooperativity between glutamate binding and photoactivation. (E) Summary of R57A experiments. Photocurrent amplitude is normalized to the amplitude of the response to 1 mM glutamate. The numbers of HEK 293T cells tested are shown in parentheses. Error bars show standard errors.