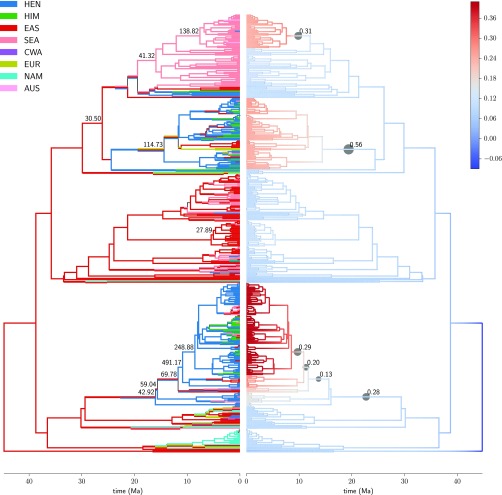
Fig. 5.
Reconstructions of ancestral geographic range (Left) and net diversification rate (Right) on the maximum clade credibility tree, with branch lengths set to posterior means, for Rhododendron. Ancestral ranges are maximum-likelihood estimates at the start and end of each branch. Net diversification values are branch-segment means of the posterior distribution estimated by BAMM. Filled circles on the right indicate branches that appear in the 95% credible set of distinct shift configurations, with the size and label of a circle indicating the cumulative probability of the branch over all configurations in the credible set. On the left, the marginal odds ratio for a shift in diversification regime along a branch is drawn for branches where the ratio exceeds 20. Geographic regions are coded as follows: AUS, Australasia; CWA, central/western Asia; EAS, temperate-boreal East Asia; EUR, Europe; HEN, Hengduan Mountains; HIM, Himalayas–QTP; NAM, North America; and SEA, Southeast Asia. Hengduan species cluster primarily in two clades, both of which show evidence of ancestral shifts to higher diversification rate in the mid-to-late Miocene.