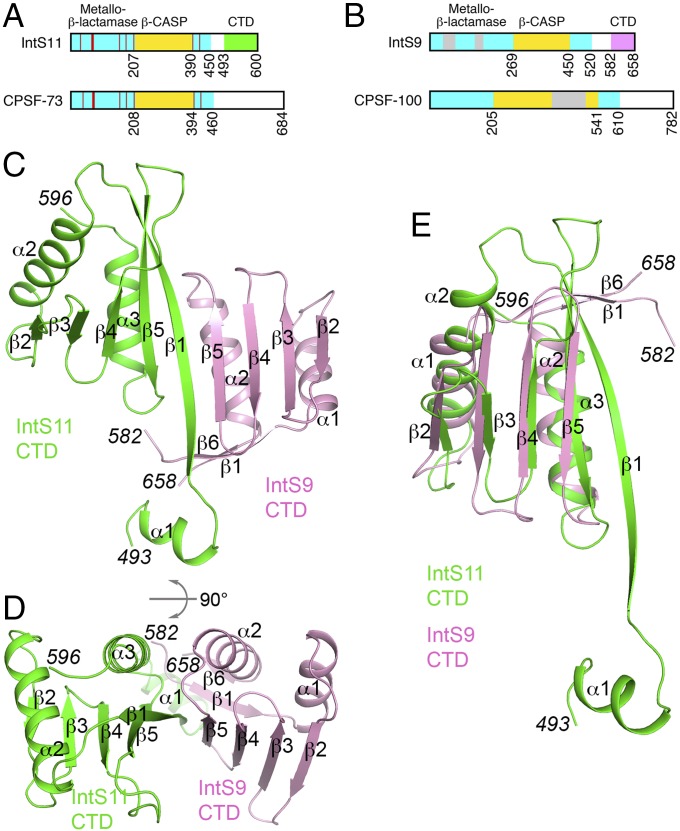
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of the human IntS9–IntS11 CTD complex. (A) Domain organizations of human IntS11 and CPSF-73. The metallo-β-lactamase and β-CASP domains are shown in cyan and yellow, respectively. The conserved residues in the active site are indicated by red lines. The CTD of IntS11 is shown in green. CPSF-73 also has a CTD, but its sequence is highly divergent from that of IntS11, and its exact boundary is not known. (B) Domain organizations of human IntS9 and CPSF-100. The CTD of IntS9 is shown in pink. An insert in the β-CASP domain of CPSF-100 and two inserts in the metallo-β-lactamase domain of IntS9 are shown in gray. (C) Structure of the human IntS9–IntS11 CTD complex. The IntS9 CTD is in pink, and the IntS11 CTD is in green. (D) Structure of the human IntS9–IntS11 CTD complex, viewed after 90° rotation around the horizontal axis. (E) Overlay of the structure of the IntS9 CTD (pink) with the structure of the IntS11 CTD (green). The structure figures were produced with PyMOL (www.pymol.org).