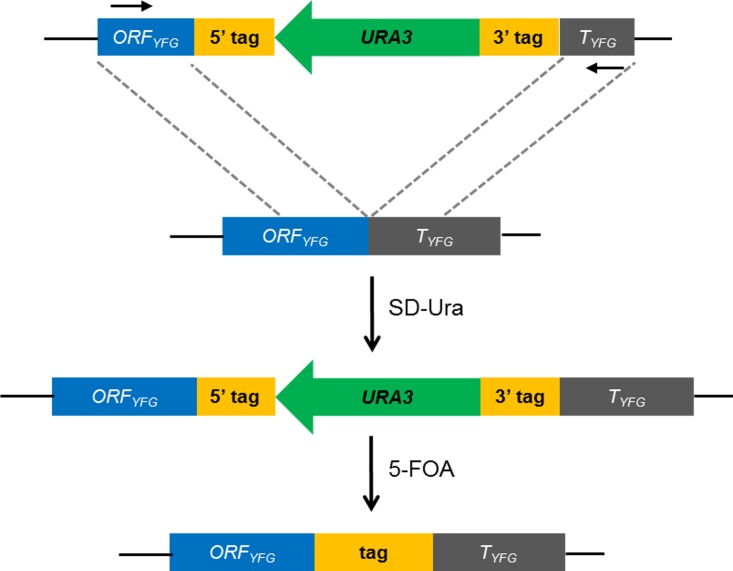
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the protein-tagging via the URA3 gene pop-in/pop-out system.
Here, we use tagging of YFG C-terminal as an example, and the N-terminal tagging of nonessential genes could be done following the same strategy. First, the ORFYFG-5′tag-URA3-3′tag-TYFG fragment is integrated into yeast chromosomes through HR using the homologous sequences of the ORF and terminator of YFG. Positive selection on an SD-Ura plate yields pop-in clones in which the designed sequence has been successfully integrated into the chromosomal locus of the YFG gene. Second, the URA3 gene would be eliminated via homologous recombination due to the duplicated sequences of 5′ and 3′ tags, leaving only one copy of the intact tag. The strains in which URA3 has been popped out are counter-selected on 5-fluoroorotic acid plates.