Figure 4.
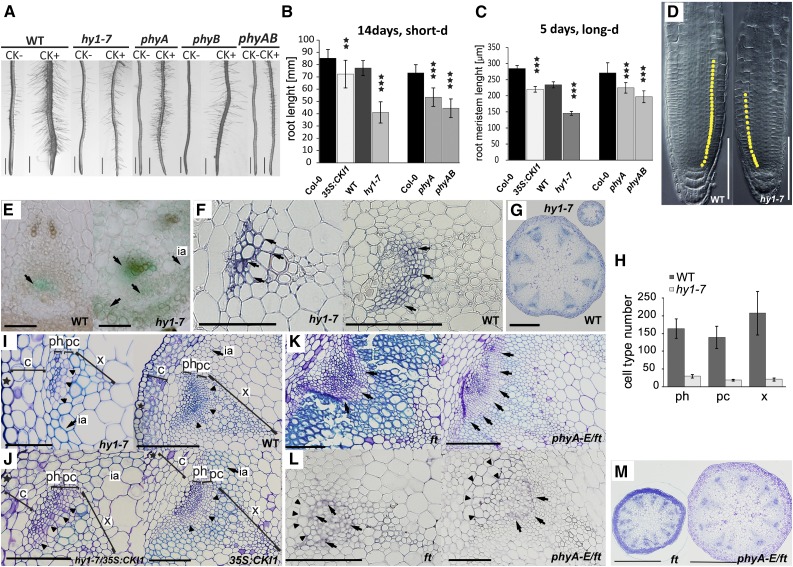
Changes in the spatiotemporal specificity of CKI1 expression are associated with changes in Arabidopsis meristematic activity. A, hy1-7 is insensitive to cytokinin with respect to root hair formation and root thickening (see also Supplemental Fig. S8). Additive loss of sensitivity to cytokinins is apparent in phyA, phyB, and phyA phyB mutants. Representative images show 14-d-old seedlings grown under short-d conditions in the presence (+) or absence (−) of cytokinin (0.1 μm BA). B to D, CKI1 is a negative regulator of root growth. Analysis of the root (B; n = 15) and the root apical meristem length (C; n = 20) in seedlings grown under white light. In comparison to wild type, hy1-7, like 35S:CKI1, has shorter roots (B) and reduced root apical meristem size (D); yellow dots in (D) indicate meristem cells. Note that the wild-type (ProCKI1:GUS) line is used as a control for hy1-7, while the Col-0 ecotype is used as a control for 35S:CKI1. Root length shortening, as well as root apical meristem reduction, is observed in the phytochrome mutants phyA and phyA phyB. Note additive effect of both phy mutations. E, ProCKI1:uidA expression profile in the vascular tissue of the inflorescence stem; arrows indicate CKI1 activity. In the wild type, CKI1 expression is predominantly localized in phloem adjacent to procambium, while in hy1-7, the CKI1 expression maximum is found mostly in the xylem. Weak activity in the phloem is also detectable. In hy1-7, up-regulation of CKI1 is apparent in the cortex, and ectopic CKI1 activity is detectable in the interfascicular arcs. F, Immunolocalization of CKI1 protein (arrows) in the vascular tissue of the inflorescence stem. In wild type, CKI1 is predominantly localized to the procambial cells, whereas the hy1-7 signal is shifted to the xylem cells. G, hy1-7 inflorescence stem show decrease in the number and size of VBs. Toluidine blue staining was used for VBs structure characterization. H, Clear reduction in numbers of all VB cell types is observed in hy1-7 (n = 3). I, Precocious lignification (light-blue stained cell walls, arrow) and reduction in the procambial cell layer (arrowheads) are observed in the basal portion of the inflorescence stem in hy1-7 when compared to wild type. Toluidine blue staining was used for VBs structure characterization. J, Partial rescue of hy1-7 phenotype by the 35S:CKI1, showing stronger, but dominantly wild-type-like (procambial) CKI1 localization (Hejátko et al., 2009). For the complementation of independent hy1-1 line, see Supplemental Fig. S9. In comparison to the parent hy1-7 line, hy1-7/35S:CKI1 reveals partial restoration of the procambial cell layer associated with increase of VB size and decreased lignification, particularly in the interfascicular arcs. Toluidine blue staining was used for VB structure characterization. K, Cross sections of the inflorescence stem of ft and phyA-E/ft mutant. In comparison to ft, phyA-E/ft reveals decrease in lignification (light-blue stained cell walls) and increased number of procambial cells (arrows). Toluidine blue staining was used for VB structure characterization. L, Immunolocalization of CKI1 protein (arrows) in the vascular tissue of ft and phyA-E/ft mutant line. Ectopic, mostly phloem localization of CKI1 in ft mutant is partially restored in the presence of phyA-E. However, ectopic CKI1 localization in the VB sheath cells (arrowheads) is still apparent in phyA-E/ft. M, Up-regulation of VBs number in ft is partially restored in the phyA-E/ft background. Toluidine-blue staining was used for VB structure characterization. Scale bars: 1 mm (A), 500 μm (G, M), 100 μm (D, E, F, I, J, K, L), and 50 μm (only for hy1-7 in E, F, and J). In all graphs, mean and sd are presented. Statistical significance determined by a t test at α-levels of 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001 (*, **, and ***, respectively) is shown. Star symbol (★), epidermal cell layer; c, cortex; ph, phloem; pc, procambium; x, xylem; ia, interfascicular arcs., long-d, long day; short d, short day.