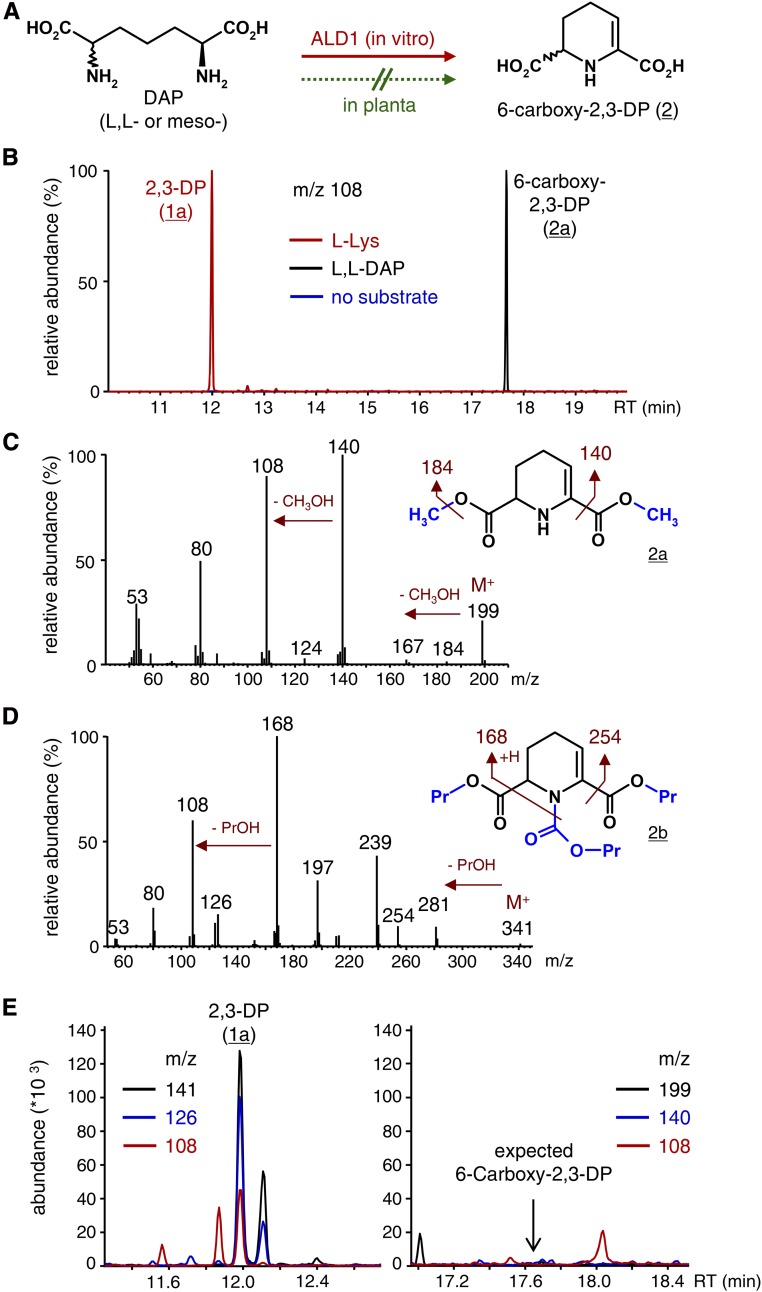
Figure 5.
ALD1 catalyzes the conversion of DAP to 6-carboxy-2,3-DP in vitro, but the conversion does not occur to detectable levels in planta. A, Reaction scheme of the in vitro conversion of l,l-DAP or meso-DAP to 6-carboxy-2,3-DP (2) by ALD1. B, In vitro ALD1 activity assays with l-Lys as the amino acid substrate (red), l,l-DAP as the amino acid substrate (black), or no amino acid substrate (blue). Pyruvate served as the acceptor oxoacid in all cases. Overlaid ion chromatograms (m/z 108) are depicted after applying workup procedure A. The m/z 108 ion occurs both in the l-Lys-derived 2,3-DP product (1a) and in the l,l-DAP-derived 6-carboxy-2,3-DP product (2a). C, Mass spectrum and chemical structure of 2a obtained from 6-carboxy-2,3-DP (2) by procedure A. The two methyl groups (blue) are introduced by derivatization. The molecular ion (M+), plausible ion fragments, and fragment losses are indicated. D, Mass spectrum and chemical structure of 2b obtained from 6-carboxy-2,3-DP (2) by procedure B. The propyl and propyl carbamate groups introduced by derivatization are depicted in blue. The molecular ion (M+), plausible ion fragments, and fragment losses are indicated. E, Segments of overlaid ion chromatograms from extract samples of Psm-inoculated Col-0 wild-type leaves, as analyzed by GC-MS procedure A. Leaf samples were harvested 48 hpi. Whereas the presence of l-Lys-derived 2,3-DP (1a) in the extracts evokes characteristic ion chromatograms (m/z 141, 126, and 108) with the expected ratios of abundance (Fig. 1C) at a retention time (RT) of 12 min (left), 6-carboxy-2,3-DP (2a; m/z 199, 140, and 108; Fig. 5C) is not detected at the supposed retention time of 17.65 min (right).