Figure 2.
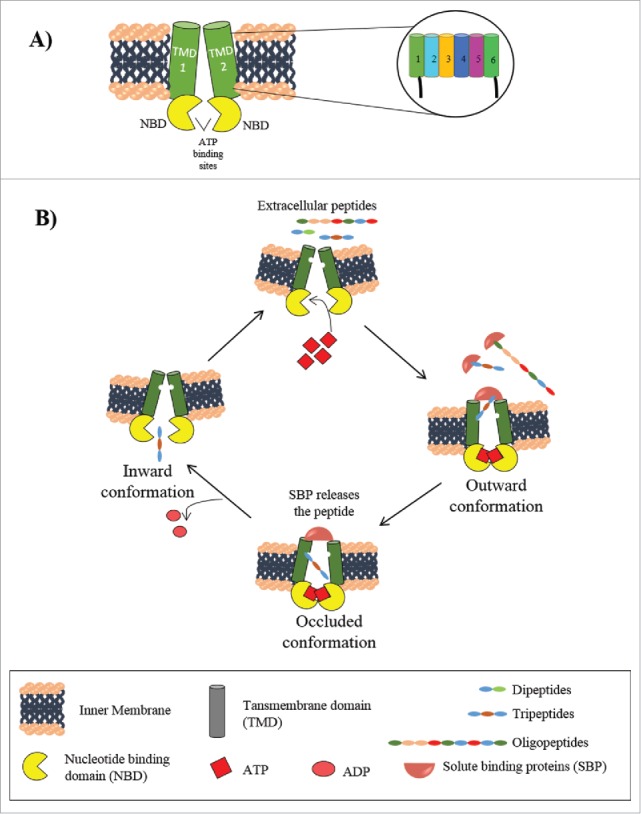
ABC peptide transporters. A. General structure of ABC transporters. A representation of single ABC transporter showing 2 transmembrane domains (TMD 1 and 2) and 2 nucleotide binding domains (NBDs) spanning the inner membrane. 6–10 transmembrane α helices constituting each TMDs are shown in enlarged view, showing a rough arrangement of the transmembrane domains. B. Mechanism of peptide transport by ABC transporters in Gram negative bacteria. The outward conformation allows the binding of 2 ATP molecules on the cytosolic face and SBP bound peptides on the extracellular face that leads to formation of the occluded conformation. ATP hydrolysis changes the conformation to the inward open state releasing the peptide in the cytoplasm.
