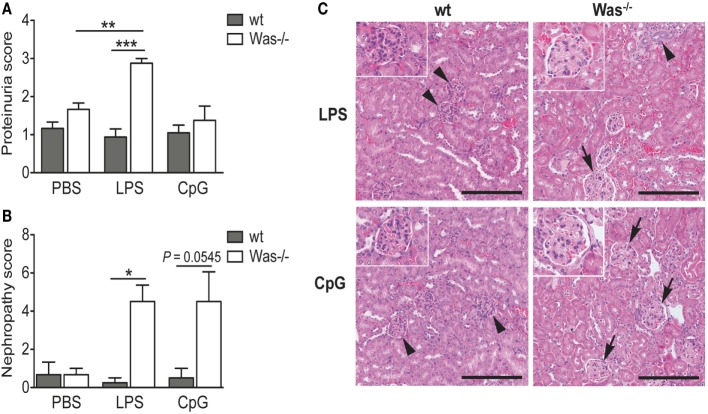
Figure 3.
Toll-like receptor-induced kidney damage in Was−/− mice. (A) Proteinuria was determined at the time of sacrifice of mice treated with PBS, LPS, or CpG (n = 5 per group), and the score was assigned starting from 0 (absence or trace of proteins, <30 mg/dL) to 4 (heavy proteinuria, >2,000 mg/dL). (B) The nephropathy score was based on the frequency and the severity of different renal lesions observed in wild-type (wt) and Was−/− mice (n = 5 per group) and ranged from 0, with no lesions, to 4, with severe histopathological changes. Mean values and SEM are reported in the graphs. The Mann–Whitney test was applied to assess whether differences between wt and Was−/− were significant (***P < 0.0001, **P < 0.005, and *P < 0.05). (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidney sections of wt and Was−/− mice after LPS or CpG treatment. Unaffected renal parenchyma with normal corpuscles is shown in wt mice (arrowheads). Glomerulopathy (arrows) characterized by segmental to global hyaline thickening of glomerular basement membrane with hypertrophic cells populating the affected mesangiocapillary areas was present in Was−/− mice. Scale bar = 200 µm (main panel) and 100 µm (inset).