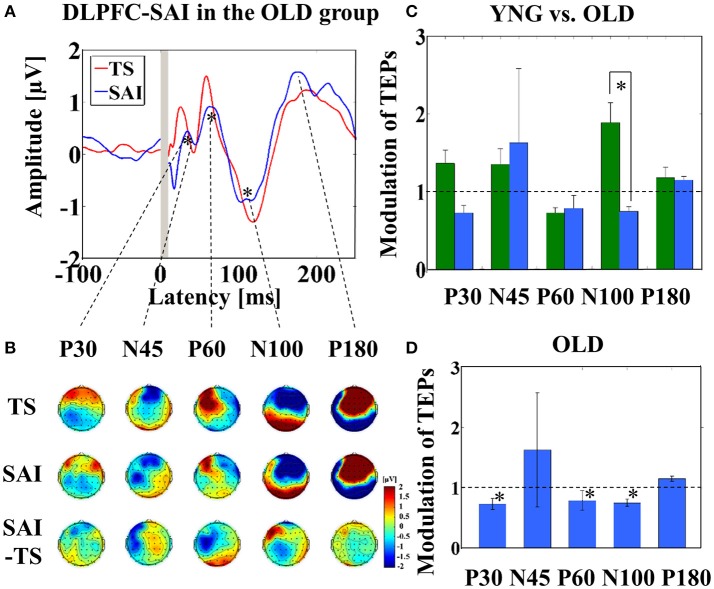
Figure 2.
Result of TEPs in the DLPFC–SAI paradigm. (A) The graph shows the TEP traces with individual SSEPs subtraction. The graph depicts TEP traces averaged across all participants for TS and SAI (ISI N20+4 ms) at the left frontal ROI. (B) The illustration shows the EEG topographical plots for TS, SAI (ISI of N20+4), and the difference between TS and SAI obtained from the DLPFC–SAI experiment. Each vertical column depicts the TEP topoplots for P30, N45, P60, N100, and P180 component from left to right, respectively. (C) The bar graph shows the group differences between younger (green bars) and older (blue bars) participants in the modulation of TEPs induced by DLPFC–SAI. The cutoff of the graph is ratio of 1. Older participants demonstrates significantly lower modulation in N100 TEP (t22 = 2.921, p = 0.008) in this paradigm. (D) The bar graph shows the modulation of TEPs within the older participants. The cutoff of the graph is ratio of 1. Older participants indicates significant modulation in P30 (t11 = 3.204, p = 0.008), P60 (t11 = 3.165, p = 0.009), and N100 (t11 = −4.871, p < 0.0001) TEPs by DLPFC–SAI. Significant findings are shown with asterisks.