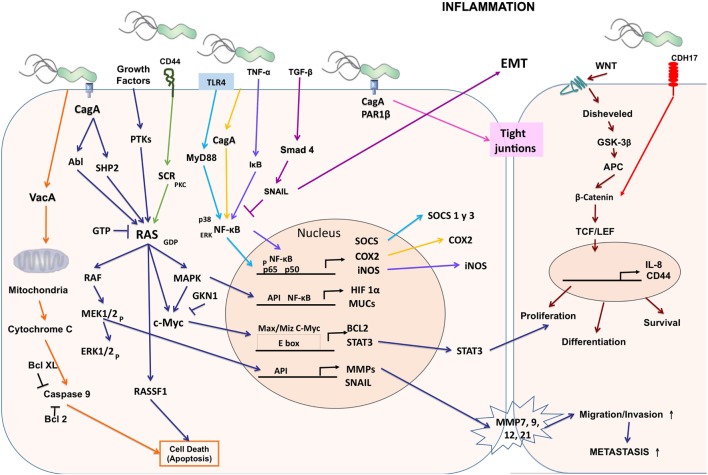
Figure 1.
Cellular and molecular pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric carcinogenesis. The phosphorylated CagA active in the SHP-2/MAPK pathway regulates MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), RAS/cMyc, and NF-κB pathways as a result of the regulation of genes such as hypoxia-inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (HIF-1α), mucins (MUCs), suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), BCL2, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and SNAIL producing proliferation, differentiation, cell survival, and increased migration, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells. CagA alters the tight junctions independently of phosphorylation. Vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) alters the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane and favors apoptosis.