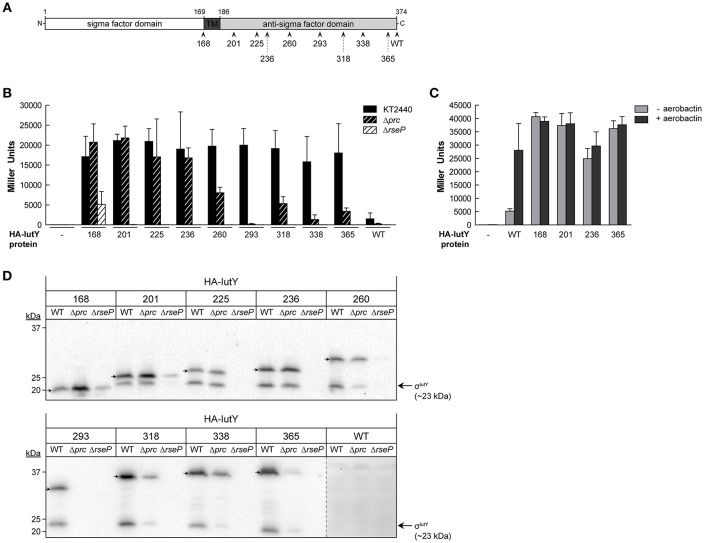
Figure 2.
Activity and processing of constitutively active truncated IutY variants. (A) Schematic representation of the P. putida sigma/anti-sigma hybrid protein IutY drawn to scale. The cytosolic sigma factor domain, transmembrane (TM) domain, and periplasmic anti-sigma factor domain are shown. The number of amino acids of the various truncated variants tested are indicated. (B) β-Galactosidase activity of the P. putida KT2440 wild-type strain (black bars) and its isogenic Δprc (black striped bars) or ΔrseP (white striped bars) mutants bearing the transcriptional fusion iutA::lacZ (pMPK4 plasmid) and a pMMB67EH-derivate expressing one of the indicated truncated IutY variants grown in LB supplemented with 1 mM IPTG. (C) β-Galactosidase activity of the P. putida ΔiutY mutant bearing the transcriptional fusion iutA::lacZ (pMPK4 plasmid) and the pMMB67EH (empty), pMMBK1-HA (WT), pMMBK1-HA-168, -201, -236, or -365 construct expressing one of the IutY variants grown in low iron medium supplemented with 1 mM IPTG in the absence (light gray bars) or presence (dark gray bars) of aerobactin. (D) The P. putida KT2440 wild-type strain (WT) and its isogenic Δprc or ΔrseP mutant expressing one of the indicated truncated IutY variants were grown in LB supplemented with 1 mM IPTG. Proteins were detected by Western-blot using an anti-HA antibody. Position of the full-length truncate protein is indicated by an arrow. The protein band corresponding to the σIutY domain and the molecular size marker (in kDa) are also indicated. Vertical dotted line indicates combination of two separate images to show prolonged exposure of the HA-IutY wild-type protein blot, which was not visible in this condition.