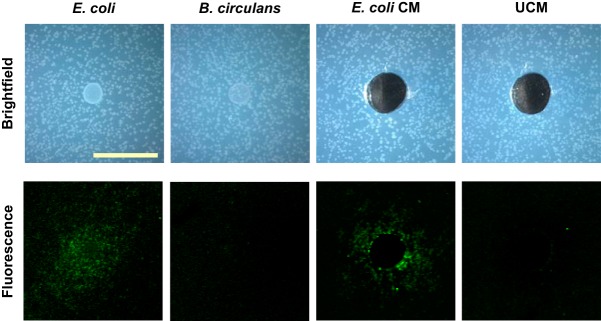
FIG 1.
E. coli promotes sporulation gene expression of B. subtilis in coculture, and the sporulation-inducing compound is secreted. Images of microcolony lawns of B. subtilis PsspB-yfp plated on agar plates either with cell suspensions of E. coli (first column) or Bacillus circulans (second column) or with wells filled with E. coli conditioned medium (CM) (third column) or unconditioned medium (UCM) (fourth column) are shown. Bright-field representative images (top row) demonstrate the configuration of the assay (scale bar = 1 cm). Representative fluorescence images (bottom row) demonstrate fluorescent B. subtilis colonies (false-colored green) around the E. coli colony and the E. coli conditioned medium but not around the negative-control colony (B. circulans) or the unconditioned medium.