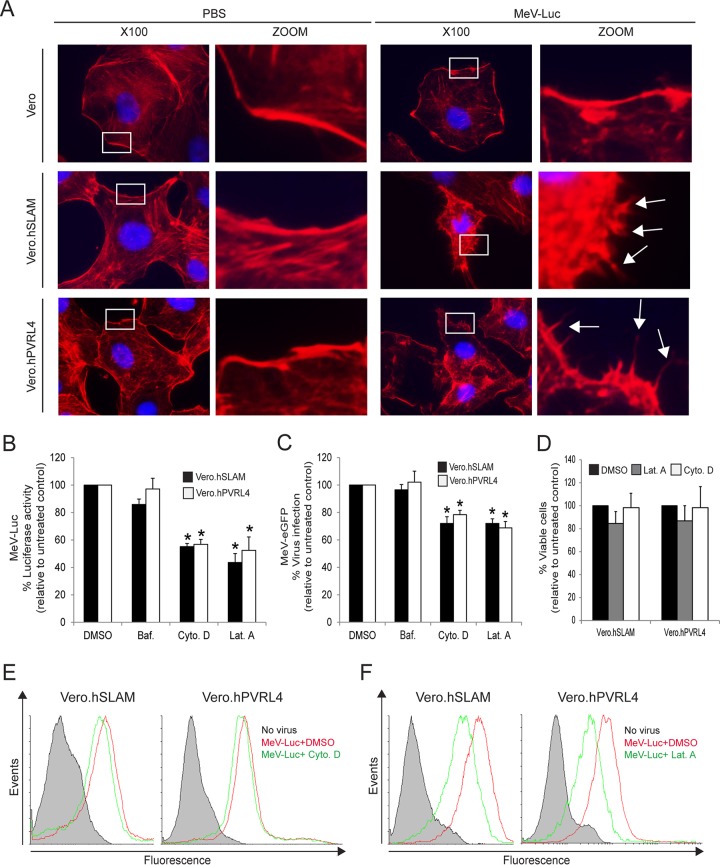
FIG 2.
Actin cytoskeleton dynamics are involved in wtMeV-Luc entry. (A) Serum-starved Vero, Vero.hSLAM, and Vero.hPVRL4 cells were exposed to wtMeV-Luc (MOI of 1) or PBS for 30 min and fixed with formaldehyde. Actin filaments were labeled with Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated phalloidin (red), and the nucleus was labeled with DAPI (blue). Images were captured with a 100× oil immersion objective. A higher magnification of the boxed area reveals the formation of actin protrusions at the cell surface membrane (arrows). Experiments were repeated 3 times, with similar results. (B and C) Vero.hSLAM and Vero.hPVRL4 cells in serum-free medium were pretreated with 500 nM bafilomycin A1 (Baf.), 40 μM cytochalasin D (Cyto. D), 1 μM latrunculin A (Lat. A), and DMSO for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were then infected with wtMeV-Luc and wtMeV-eGFP at an MOI of 1. (B) As a measure of cell entry by wtMeV-Luc, bioluminescence was measured at 8 hpi and is displayed as a percentage of luciferase activity relative to that under untreated conditions (DMSO). Both cytochalasin D and latrunculin A treatments inhibited MeV-Luc entry into Vero hSLAM and Vero hPVRL4 cells. (C) After wtMeV-eGFP infection, the inoculum was removed and replaced with fresh medium containing 200 μM FIP to prevent secondary infection. Twenty hours later, virus infectivity was measured by FACS analysis and is displayed as a percentage of eGFP-positive cells relative to that under untreated conditions (DMSO). Bafilomycin, cytochalasin D, and latrunculin A treatments had no effect upon MeV-eGFP infection. (D) To test for potential drug toxicity, Vero.hSLAM and Vero.hPVRL4 cells in serum-free medium were pretreated with 40 μM cytochalasin D, 1 μM latrunculin A, and DMSO for 30 min at 37°C. Toxicity assays, using the MTS-based assay described in Materials and Methods, were performed, and results are displayed as a percentage of viable cells relative to those under untreated conditions (DMSO). No toxicity due to cytochalasin D or latrunculin A was observed at the concentrations tested. (E and F) To determine effects on virus binding, Vero.hSLAM and Vero.hPVRL4 cells were pretreated with DMSO, cytochalasin D (E), and latrunculin A (F) as indicated above and then incubated with wtMeV-Luc at an MOI of 10 for 1.5 h. Cells were incubated with an MeV anti-H primary antibody followed by an Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody to detect MeV-bound cells by FACS analysis. Cells incubated in the absence of virus (no virus) (filled histograms) were stained with anti-MeV hemagglutinin antibody. Experiments were repeated 3 times, with similar results. Data from one representative experiment are shown in panels E and F. The studies showed that cytochalasin D had no effect and that latrunculin A had a minimal effect on cell binding to MeV-Luc. The results shown in panels B to D are expressed as the means of data from 3 independent experiments, and the error bars indicate standard deviations. Statistically significant differences (P < 0.05 by ANOVA) are indicated by asterisks.