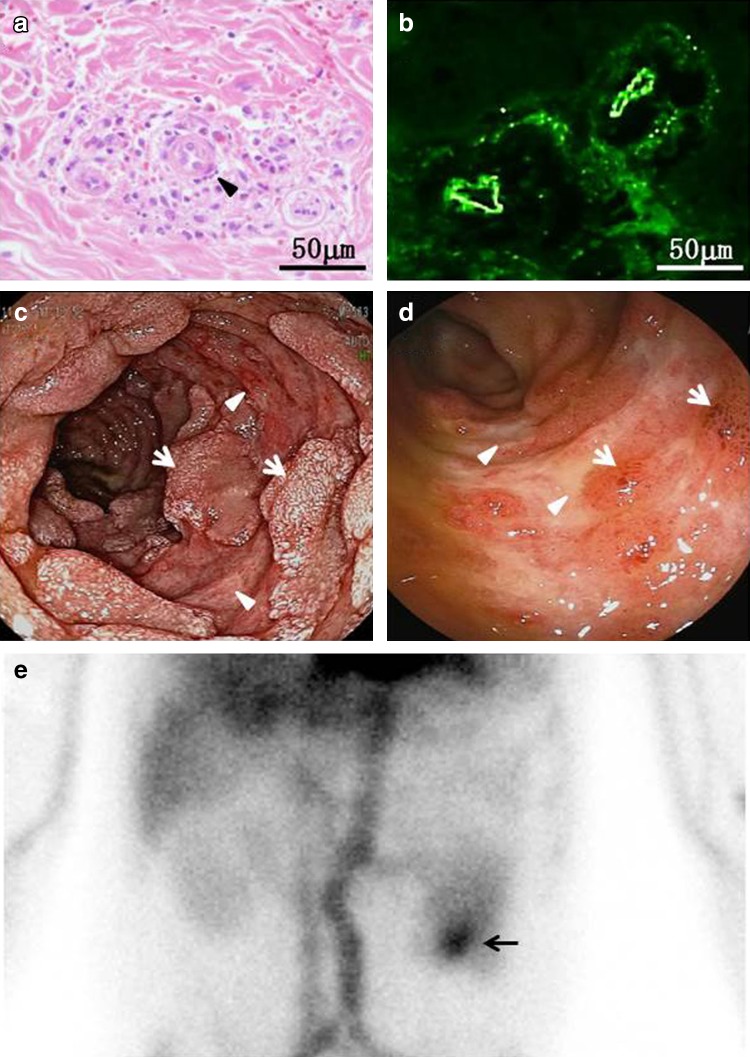
Fig. 2.
The skin biopsy (a, b), endoscopy (c, d) and scintigraphy findings (e). A punch-biopsy specimen of the skin obtained from the lower extremity revealed leukocytoclastic vasculitis in the superficial dermis, with the infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, leukocytoclasis (arrowhead) and extravasation of RBCs adjacent to small venules (a). Direct immunofluorescence studies revealed deposition of IgA in the walls of the involved dermal vessels (b). During upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, the antrum of the stomach was unremarkable, while there were multiple raised petechiae associated with diffuse linear ulcers (arrowheads) with friability in the descending duodenum. Note the presence of scattered residual mucosal tissues (arrows) (c). Total colonoscopy showed scattered ulcerative lesions (arrowheads) associated with sporadic mucosal ecchymosis (arrows) in the terminal ileum (d). Planar images of the anterior abdomen with 99mTc-HSA showed the accumulation of the radiotracer, which indicated presumable jejunum bleeding (arrow), 60 min post-injection (e)