Figure 1.
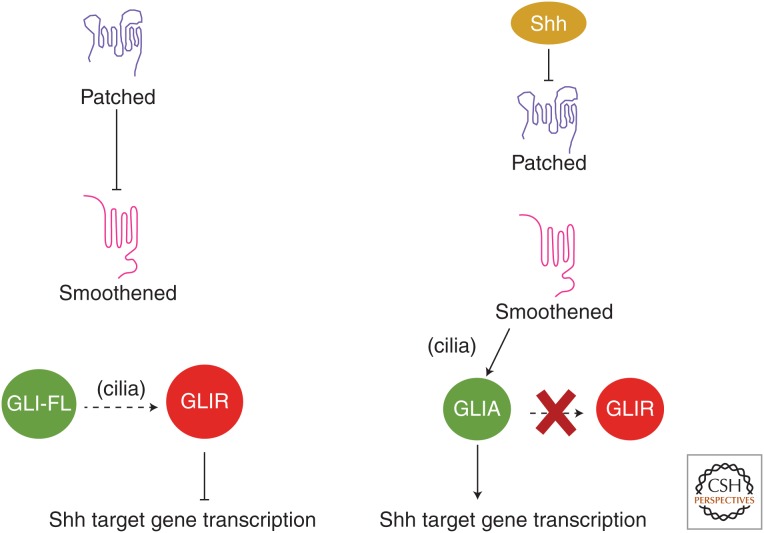
The backbone of the Hedgehog (Hh) signal transduction pathway. The core of the Hh signaling pathway is conserved between Drosophila and vertebrates. In the absence of ligand, the Hh receptor Patched (PTCH1) keeps the pathway off by inhibiting the activity of the seven transmembrane-domain protein Smoothened (SMO). When SMO is inactive, the GLI/Ci (glioblastoma/Cubitus interruptus) transcription factors are proteolytically processed to make a transcriptional repressor that binds to Hh target genes and blocks their transcription. Binding of Hh to PTCH1 inhibits its activity, relieving the repression of SMO, which promotes conversion of full-length GLI/Ci into a transcriptional activator. In vertebrates, cilia are required for the production of both GLI-repressor and GLI-activator.