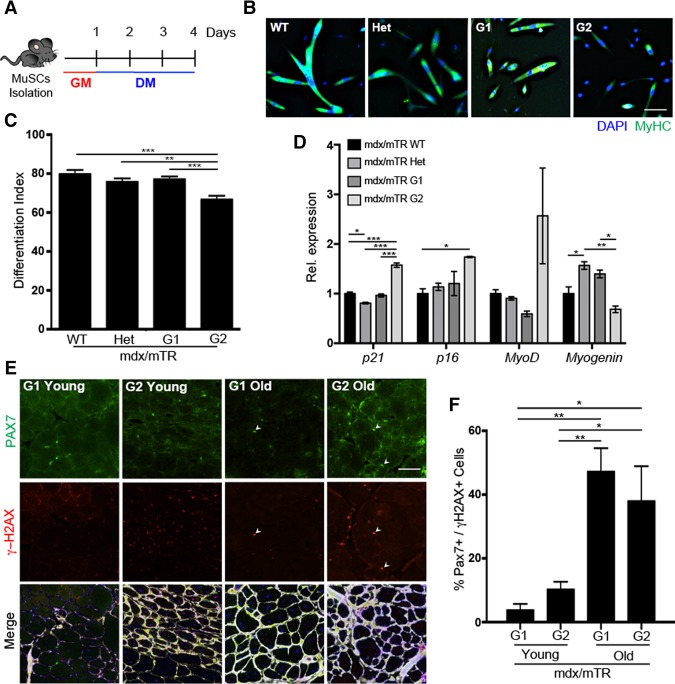
Figure 1.
MuSCs isolated from mdx/mTR mice display impaired differentiation, up-regulation of senescence markers, and DNA damage accumulation through disease progression. (A) Schematic representation of a MuSC differentiation experiment. (B) Immunofluorescence for MyHC (green) and DAPI (4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole) (blue) in MuSCs isolated from 9.5- to 11-mo-old mice and induced to differentiate for 3 d. (C) Differentiation index. (D) Quantitative PCR (qPCR) on isolated MuSCs from mdx/TR wild-type (WT), heterozygous (Het), G1, and G2 mice normalized for GAPDH. (E) Immunofluorescence for PAX7 (green), γH2AX (red), Laminin (white), and DAPI (blue) in gastrocnemius muscles isolated from 2-mo-old (young) and 18- to 24-mo-old (old) mdx/mTR mice. (F) Quantification of PAX7- and γH2AX-coexpressing cells. Bar, 25 µm.