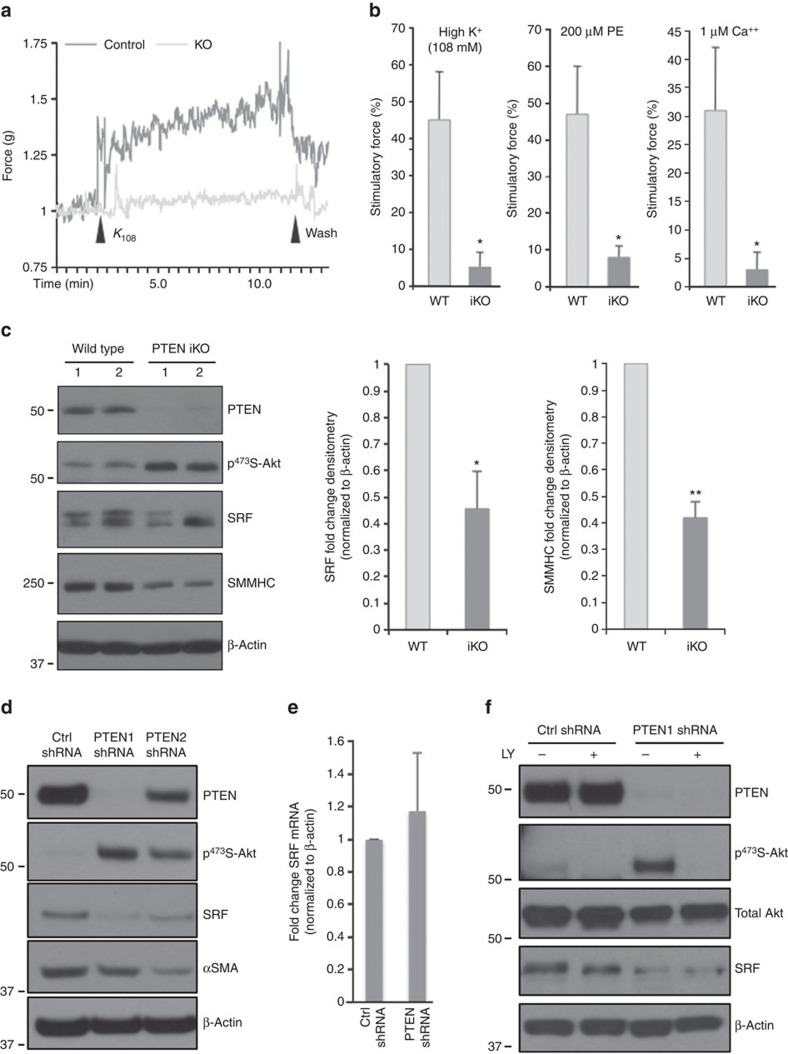
Figure 1. PTEN-dependent vessel contractility and serum response factor (SRF) activity.
Wild-type (WT) and inducible PTEN knockout (PTEN iKO) mice were generated and treated with tamoxifen as described in Methods. (a,b) Isometric force normalized to vessel length was measured in isolated aortic rings from WT and PTEN iKO mice exposed to the indicated concentrations of potassium chloride (K+), phenylephrine (PE) or calcium chloride (Ca++). (a) Representative tracing from potassium-stimulated aortic rings. (b) Quantification of force generation. Data represent averages±s.e.m. from six (K+, PE) or four (Ca++) vessels per group. *P<0.01 versus WT. (c) Western blot analysis for PTEN, phospho-Akt, SRF and SM myosin heavy chain (SM-MHC) in whole cell lysates (WCL) of aortic media from WT or PTEN iKO mice. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Left—representative blot from two mice per genotype; each lane represents an individual mouse. Right—fold changes in densitometry measurements±s.e.m. N=12; *P=0.016; **P=0.000056 versus WT. (d,e) Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) stably expressing control (Ctrl) or PTEN-specific shRNA were serum-restricted for 24 h (RNA) or 48 h (protein). (d) WCL were analysed for total PTEN, phospho-Akt, SRF and αSMA. (e) Total RNA was analysed by qPCR for SRF mRNA. Shown are fold changes in SRF mRNA copy number±s.e.m. from six independent experiments. (f) Ctrl and PTEN-deficient SMCs were serum-restricted in the presence or absence of the PI3-kinase inhibitor, LY294002 (10 μM) for 24 h. WCL were analysed for total PTEN, phospho-Akt, total Akt and SRF levels. N=3 independent experiments. Molecular weight markers were cropped out for final SRF blots; please see Supplementary Fig. 8. qPCR, quantitative PCR.