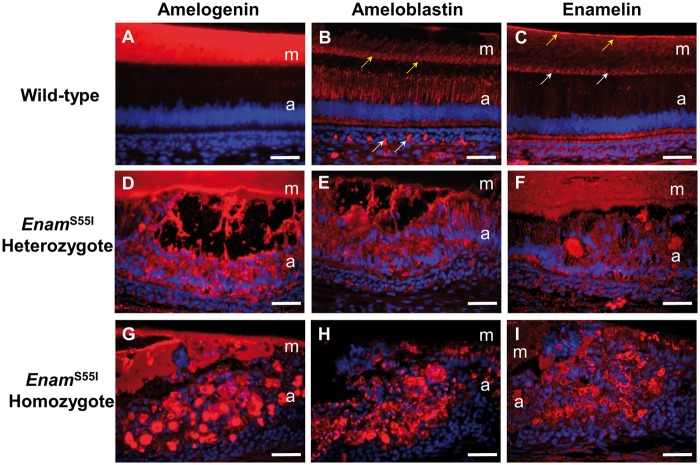
Figure 2.
Enamel matrix protein distribution in EnamS55I mutant mice. (A–C) Wild-type mice. (A) Strong amelogenin immunoreactivity in the extracellular matrix of wild-type mice. (B) Ameloblastin immunoreactivity can be seen within the ameloblasts and at the secretory front (yellow arrows) of the matrix and extending as parallel lines into it. There is non-specific immunolabelling of the vasculature below the ameloblasts (white arrows). (C) Enamelin shows strong immunoreactivity at the dentino-enamel junction (yellow arrows) and at the secretory front (white arrows) with less intense immunostaining throughout the remainder of the matrix. (D–F) EnamS55I heterozygous mice. (D) In EnamS55I heterozygous mice there is strong amelogenin immunoreactivity in the matrix and within the ameloblasts. (E) Little immunoreactivity is observed in the matrix of heterozygous mice but there is strong intracellular immunolabelling for ameloblastin in the ameloblasts. (F) Strong enamelin immunoreactivity is seen throughout the matrix and within the ameloblasts. (G–I) EnamS55I homozygous mice. (G) There is intense amelogenin immunoreactivity both in the matrix and within the ameloblasts. (H) Strong ameloblastin immunolabelling is confined to the ameloblasts. (I) There is strong enamelin immunoreactivity within the ameloblasts and weaker immunostaining of the matrix. a: ameloblasts; m; matrix. Scale bars: 50 μm.