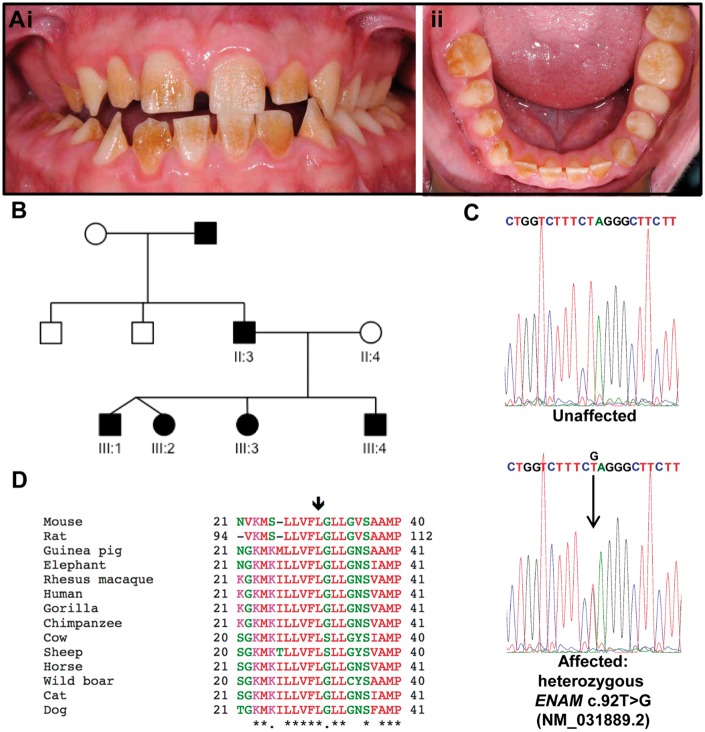
Figure 7.
(Ai and ii) The permanent dentition of III:4 is characterized by a generalized rough hypoplastic AI with superficial exogenous staining. (B) Pedigree of family 1. Individuals are not necessarily shown in age order. Affected individuals are indicated by shading. DNA was available from labelled individuals. Whole exome sequencing was carried out using DNA from III:2. Teeth were obtained from III:1 and III:4. (C) Sanger sequencing of ENAM exon 3 confirmed the heterozygous c.92T > G variant (NM_031889.2), originally identified in III:2 by WES, segregated with the disease phenotype in all available family members. (D) Clustal Omega multiple sequence alignment of homologous ENAM protein sequences. The arrow indicates the residue altered by the c.92T > G variant, p.L31R (NM_031889.2; NP_114095.2). The affected residue and the ten residues that flank it to either side are included in the alignment. ENAM sequences used: Mouse, Mus musculus NP_059496.1; Rat Rattus norvegicus NP_001099471.1; Guinea pig, Cavia porcellus XP_003467585.2; Elephant, Loxodonta africana XP_003414215.1; Rhesus macaque, Macaca mulatta XP_014994062.1; Human, Homo sapiens NP_114095.2; Gorilla, Gorilla gorilla XP_004038829.1; Chimpanzee, Pan troglodytes XP_526591.1; Cow, Bos taurus XP_605463.4; Sheep Ovis aries XP_004009936.1; Horse Equus caballus XP_001487944.1; Wild boar, Sus scrofa NP_999406.1; Cat, Felis Catus XP_003985351.1; Dog Canis lupus familiaris XP_539305.3.