Figure 3.
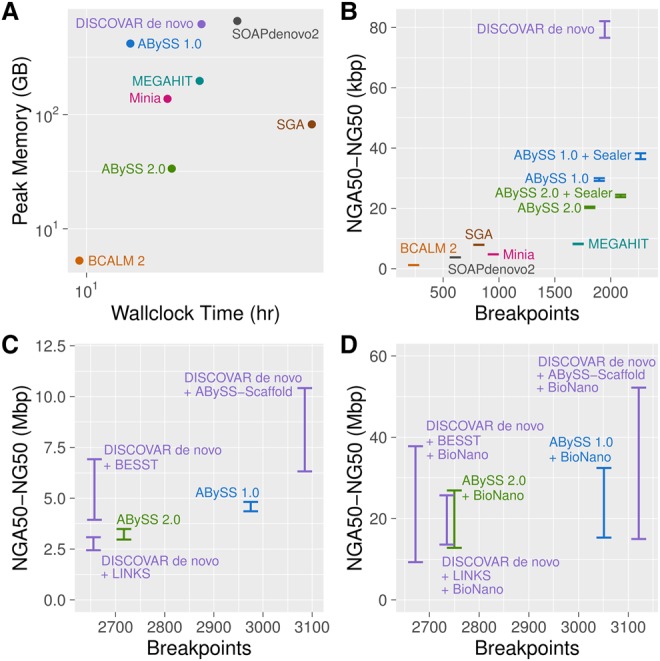
De novo assembly results for Genome in a Bottle HG004 human genome short-read data with ABySS 1.0, ABySS 2.0, BCALM 2, DISCOVAR de novo, MEGAHIT, Minia, SOAPdenovo2, and SGA. To enable comparison with ABySS, the DISCOVAR de novo assembly was scaffolded with third-party scaffolders ABySS-Scaffold, LINKS (Warren et al. 2015), and BESST (Sahlin et al. 2016). For panels B–D, on the y-axes we show the range of NGA50 to NG50 to indicate uncertainty caused by real genomic variants between individual HG004 and the reference genome (GRCh38). On the x-axes, we show the number of breakpoints that occurred when aligning the sequences to the reference genome. (A) Peak memory usage and wall-clock time for the assemblers. (B) Contiguity and correctness metrics for contig sequences. (C) Contiguity and correctness metrics after scaffolding with mate-pair (MPET) reads. The SOAPdenovo2 result for this plot was excluded as an outlier with an NGA50 (NG50) value of 103 kbp (172 kbp) and 10,610 breakpoints. (D) Contiguity and correctness metrics after further scaffolding with BioNano optical mapping data, using BioNano's hybrid scaffolding pipeline.
