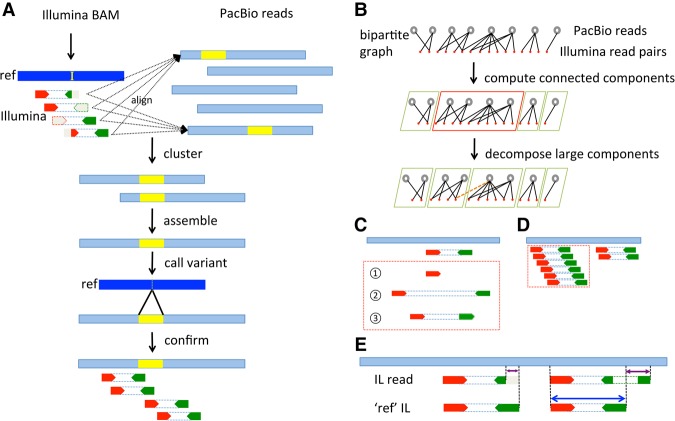
Figure 1.
Diagram of HySA for SV assembly and detection. (A). Abnormally aligned Illumina reads are extracted from a BAM file and aligned to a set of PacBio reads (light blue) generated from the same DNA sample. The cluster of reads associated with an SV is identified using a set of bipartite-graph partitioning algorithms. Contigs are assembled from PacBio reads in each cluster and are aligned to the reference, from which SVs and breakpoints are identified and further confirmed by Illumina reads in the same cluster. An insertion (yellow segment in the reference and yellow segments in PacBio reads) is used for illustration. The Illumina reads are in red and green, corresponding to the forward and the reverse strands, respectively. The subsequence or whole read that cannot be mapped is in gray. (B) Clustering strategy. A bipartite graph is built from the pairwise alignment of Illumina reads to PacBio reads. One set of the nodes corresponds to PacBio reads (top row, black open circles), and the other set corresponds to Illumina read pairs (second row, red solid circles). An edge is added when there is a reliable alignment between an Illumina read pair and a PacBio read. The bipartite graph is decomposed into connected components (green and red boxes) using the Union-Find algorithm. Large components, e.g., the one in the red box, are further decomposed into communities of expected sizes using a graph decomposition algorithm called Infomap. (C) False alignments between Illumina and PacBio reads are illustrated in dashed red box: (1) single-end alignments; (2) paired ends with abnormal insert size; and (3) paired ends with abnormal orientation. (D) False alignments due to repetitive regions. Illumina read alignments against a PacBio read (dotted red box) are filtered out when the depth of Illumina reads significantly exceeds the expected coverage. (E) A competitive alignment strategy that eliminates false alignments between PacBio and Illumina reads. For each Illumina read pair, a pseudo (ref) read pair is synthesized from the reference sequence in identical positions and orientations. An alignment between an Illumina read pair and a PacBio read is false when (1) the Illumina pair has a shorter aligned sequence against the PacBio read than does its pseudo pair (left), or (2) the alignment of the Illumina pair has a split whereas the pseudo pair does not (right).