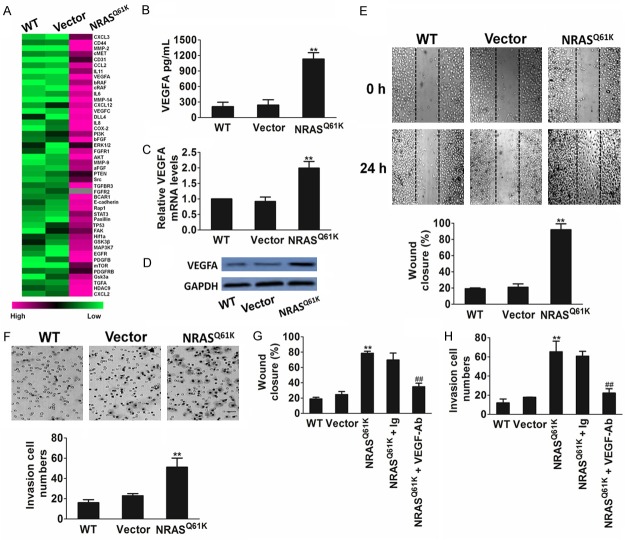
Figure 2.
NRASQ61K knock-in increases VEGFA-mediated migration of HUVECs. A. NRASQ61K up-regulates the expression of pro-angiogenic factors in NRASQ61K knock-in BEAS-2B cells. Gene expression analysis was performed by real-time PCR comparing parental BEAS-2B with NRASQ61K clone. Differentially modulated genes were selected and analyzed by hierarchical clustering. B. Quantification of secreted VEGFA in BEAS-2B cells by ELISA. Data are from three independent experiments and are mean ± SD. n = 3, **P < 0.01 compared with wild type cells. C. Effect of NRASQ61K on VEGFA gene mRNA level. BEAS-2B cells were treated with NRASQ61K plasmid or vector, and VEGFA mRNA level were detected by real-time PCR. Data are from three independent experiments and are mean ± SD. n = 3, **P < 0.01 compared with wild type cells. D. Western blot shown that the expression of VEGFA was increased in cells transfected with NRASQ61K plasmid. Data were from three independent experiments. E. Migration of HUVECs was enhanced by the supernatant of BEAS-2B NRASQ61K knock-in cells compared with the wild type counterpart. Scale bar represents 50 μm. F. Invasion of HUVECs was enhanced by the supernatant of BEAS-2B NRASQ61K knock-in cells compared with the wild type BEAS-2B cells. Scale bar represents 50 μm. G and H. VEGFA blocking antibody (VEGFA-Ab) abolished NRASQ61K-induced cell migration and invasion. Data are from three independent experiments and are mean ± SD. n = 3, **P < 0.01 compared with wild type cells. ##P < 0.01 compared with NRASQ61K knock-in cells.