Figure 5.
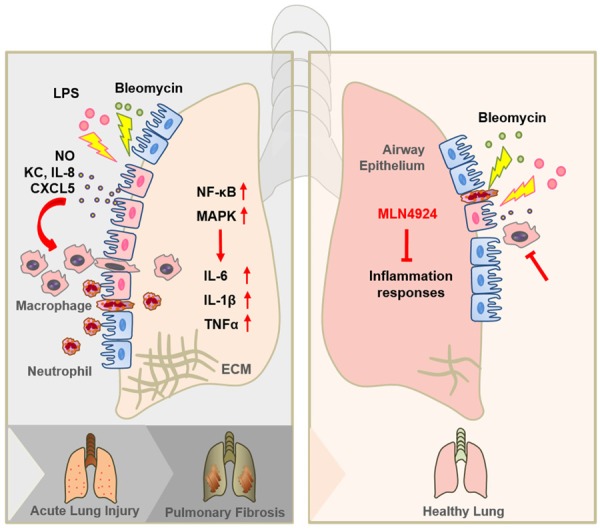
Graphic abstract of MLN4924 protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the early inflammatory process. When lung injury occurs, the airway epithelia firstly detect the injury and recruit inflammatory cells by secreting chemokines, such as KC, IL-8 and CXCL5. Recruited inflammatory cells, including macrophages and neutrophils, trigger inflammation by producing NO and several cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1β and TNFα, and thus contributing to acute lung injury. When the injury proceeds, extracellular matrix (ECM) begins to form and deposit, which at last leads to pulmonary fibrosis. MLN4924 can effectively block the production of chemokines from the airway epithelia as well as NO and cytokines from the inflammatory cells. By this mechanism MLN4924 suppresses the recruitment of inflammatory cells and the initiation of inflammation responses.
