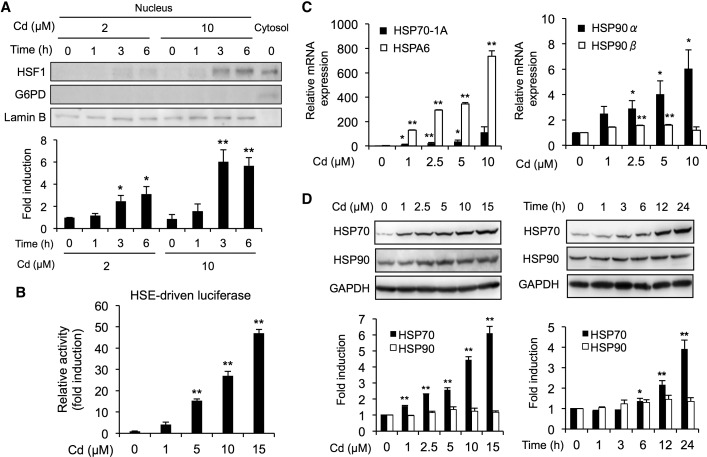
FIG. 1.
Activation of the HSF1/HSE pathway by cadmium in BAECs. A, Translocation of HSF1 into the nucleus by cadmium. Cells were exposed to cadmium chloride (2 or 10 µM) for 1, 3, or 6 h, then the nucleus and cytosol fractions were subjected to Western blotting analysis using the antibodies indicated. G6PD and Lamin B were used as cytosolic maker and nucleus marker, respectively. B, Activation of HSE-driven transcriptional luciferase activity by cadmium. The HSE-driven luciferase activity was measured using cells that had been exposed to cadmium chloride (1, 5, 10, or 15 µM) for 12 h. C, Cadmium-mediated upregulation of heat shock protein (HSP) mRNA expression. Cells were exposed to cadmium chloride (1, 2.5, 5, or 10 µM) for 12 h, then real-time PCR analyses was performed for the HSP70-A1, HSPA6, HSP90α, and HSP90β genes. D, Increase in HSP proteins caused by exposure to cadmium. Cells were exposed to cadmium chloride (1, 2.5, 5, or 10 µM) for 24 h, then the total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting analysis using the antibodies indicated. Each value is the mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments. * P < .05 and ** P < .01 compared with the controls.